Concordance of Radiological and Histopathological Features in a Monosodium Iodoacetate–Induced Osteoarthritis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i10.20Keywords:
Osteoarthritis, K&L Score, Oarsi Score, Monoiodoacetate, Rat ModelAbstract
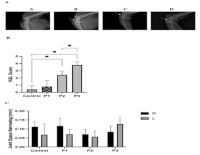
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease characterized by progressive impairment of joint function involving cartilage and synovium. Although histopathological examination remains the gold standard for confirming OA, radiological assessment in small-animal models is less frequently reported. In this study, we evaluated the concordance between radiological and histopathological OA features in a rat model induced by intra-articular injection of monosodium iodoacetate (MIA). Twenty male Wistar rats were divided evenly into four groups (Control, P1, P2, P3), with the latter three groups receiving 2 mg/kg of MIA in the right knee. Radiological (Kellgren–Lawrence) and histopathological (OARSI) scores were assessed at days 7 (P1), 14 (P2), and 21 (P3). Compared to the control, both K&L and OARSI scores were significantly elevated on days 14 and 21 (p < 0.001). Radiological and histological features showed good concordance over time, revealing clear, progressive OA-like changes by day 21. Our study revealed that the histopathology of features in experimental OA by using MIA has significant concordance with the radiographic manifestation.
References
1. Townsend K, Imbert I, Eaton V, Stevenson G. W, King T. Voluntary exercise blocks ongoing pain and diminishes bone remodeling while sparing protective mechanical pain in a rat model of advanced osteoarthritis pain. Pain. 2022; 163(3), E476–E487. Doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000002392
2. He Y, Li Z, Alexander P. G, Ocasio-Nieves B. D, Yocum L, Lin H, Tuan R. S. Pathogenesis of osteoarthritis: Risk factors, regulatory pathways in chondrocytes, and experimental models. Biology. 2020; 9(8), 1–32. Doi.org/10.3390/biology9080194
3. Vasilceac FA, Marqueti R. de C, Neto IV. de S, Nascimento D. da C, Souza M. C. de, Durigan JLQ, Mattiello S. M. Resistance training decreases matrix metalloproteinase-2 activity in quadriceps tendon in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2021; 25(2), 147–155. Doi.org/10.1016/j.bjpt.2020.03.002
4. Rannou F, Pelletier JP, Martel-Pelletier J. Efficacy and safety of topical NSAIDs in the management of osteoarthritis: Evidence from real-life setting trials and surveys. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016; 45(4), S18–S21. Doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.11.007
5. Nagira K, Ikuta Y, Shinohara M, Sanada Y, Omoto T, Kanaya H, Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Adachi N, Miyaki S, Lotz M. Histological scoring system for subchondral bone changes in murine models of joint aging and osteoarthritis. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1), 1–14. Doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66979-7
6. Orita S, Koshi T, Mitsuka T, Miyagi M, Inoue G, Arai G, Ishikawa T, Hanaoka E, Yamashita K, Yamashita M, Eguchi Y, Toyone T, Takahashi K, Ohtori S. Associations between proinflammatory cytokines in the synovial fluid and radiographic grading and pain-related scores in 47
consecutive patients with osteoarthritis of the knee. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011; 12(1), 144. Doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-12-144
7. Shinde M, Pardeshi D, Patel M, Bhardwaj L, Sarwey K. Grading of Knee Osteoarthritis Based on Kellgren-Lawrence Classification and Finding an Association Between Radiographic Features and Pain : A Cross-Sectional Study at a Tertiary Health Care Hospital. Cureus. 2024; 16(11). Doi.org/10.7759/cureus.73224
8. Ashinsky BG, Colleta CE, Bouhrara M, Lukas VA, Boyle JM, Reiter DA, Neu CP, Goldberg IG, Spencer RG. Machine learning classification of OARSI-scored human articular cartilage using magnetic resonance imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016; 23(10), 1704–1712. Doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2015.05.028.
9. Pascual-Garrido C, Kikuchi K, Clohisy JC, O’Keefe RJ, Kamenaga T. Revealing a Natural Model of Pre-Osteoarthritis of the Hip Through Study of Femoroacetabular Impingement. HSS J. 2023; 19(4), 434–441. Doi.org/10.1177/15563316231190084
10. Sifre V, Ten-Esteve A, Serra CI, Soler C, Alberich-Bayarri Á, Segarra S, Martí-Bonmatí L. Knee Cartilage and Subchondral Bone Evaluations by Magnetic Resonance Imaging Correlate with Histological Biomarkers in an Osteoarthritis Rabbit Model. Cartilage. 2022; 13(3). Doi.org/10.1177/19476035221118166
11. Kuyinu EL, Narayanan G, Nair LS, Laurencin CT. Animal models of osteoarthritis: Classification, update, and measurement of outcomes. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2016; 11(1), 1–27. Doi.org/10.1186/s13018-016-0346-5
12. Mohd Heikal MY, Ahmad Nazrun S, Chua KH, Norzana AG. Stichopus chloronotus aqueous extract as a chondroprotective agent for human chondrocytes isolated from osteoarthitis articular cartilage in vitro. Cytotechnology. 2019; 71(2), 521–537. Doi.org/10.1007/s10616-019-00298-2
13. Longo UG, Papalia R, De Salvatore S, Picozzi R, Sarubbi A, Denaro V. Induced Models of Osteoarthritis in Animal Models: A Systematic Review. Biology. 2023; 12(2), 1–17. Doi.org/10.3390/biology12020283
14. Takahashi I, Matsuzaki T, Kuroki H, Hoso M. Induction of osteoarthritis by injecting monosodium iodoacetate into the patellofemoral joint of an experimental rat model. PLoS ONE. 2018; 13(4), 1–15. Doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196625
15. Bao Z, Chen M, Li C, Shan Q, Wang Y, Yang W. Monosodium iodoacetate-induced subchondral bone microstructure and inflammatory changes in an animal model of osteoarthritis. Open Life Sci. 2022; 17(1), 781–793. Doi.org/10.1515/biol-2022-0079
16. Ise S, Ochiai N, Hashimoto E, Hirosawa N, Kajiwara D, Shimada Y, Inagaki K, Hiraoka Y, Hattori F, Ohtori S. Evaluation of articular changes using a rat mono‐iodoacetate‐induced shoulder. J Orthop Res. 2022; 41(11), 2359–2366. Doi.org/10.1002/jor.25560
17. Mohan G, Perilli E, Kuliwaba JS, Humphries JM, Parkinson IH, Fazzalari NL. Application of in vivo micro-computed tomography in the temporal characterisation of subchondral bone architecture in a rat model of low-dose monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13(6), R210. Doi.org/10.1186/ar3543
18. Yoh S, Kawarai Y, Hagiwara S, Orita S, Nakamura J, Miyamoto S, Suzuki T, Akazawa T, Shiko Y, Kawasaki Y, Ohtori S. Intra-articular injection of monoiodoacetate induces diverse hip osteoarthritis in rats, depending on its dose. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022; 23(1), 1–10. Doi.org/10.1186/s12891-022-05454-y
19. Sandra F, Rizal MI, Dewi NM, Kukita T. Caffeic acid inhibits swelling, bone loss, and osteoclastogenesis in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats. Indones Biomed J. 2022; 14(3): 276-81. Doi.org/10.18585/inabj.v14i3.2033
20. Dasiman R, Malek MA, Bahari EA, Zakaria FN, Hashim NK, Samsudin A, Daud KA, Sham F, Amom Z. Effect of Croton caudatus Geiseler aqueous root extract on reproductive and biochemical parameters in male Wistar rats. Indones Biomed J. 2020; 12(3): 251-60. Doi.org/10.18585/inabj.v12i3.1186
21. Butar Butar J, Wijayanti Z, Tjahyana B, Sunggono V, Harianto H. (2013). Association of cross-linked C-telopeptide II collagen and hyaluronic acid with knee osteoarthritis severity. Indones Biomed J. 2013; 5(3): 179-84. Doi.org/10.18585/inabj.v5i3.69
22. Handono K, Prasetyo DA, Kurnianingsih N, Wahono CS, Albaar TM. Impact of walking exercise intensity on cartilage IL-1, TNF-α, IL-4, MMP-13 and pain threshold in osteoarthritis rat models. Narra J. 2025; 5 (2): e2109. Doi.
23. Handono K, Prasetyo DA, Kurnianingsih N, Wahono CS. Effects of Walking Exercise and Meloxicam on MMP-13 Expression and Pain Threshold in Osteoarthritis. Trop J Nat Prod Res 2025; 9(3), 1118 – 1122. Doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i3.29
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Tropical Journal of Natural Product Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.







