Topical Application of Geniotrigona thoracica Propolis Nanoparticle for Wound Healing in Streptozotocin-induced Type-1 Diabetic Rat Model
Main Article Content
Abstract
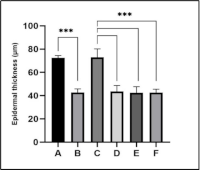
Diabetic ulcers are common complications of diabetes. Herbal products such as propolis may accelerate wound healing because of their biological activity. The development of propolis using nanotechnology is expected to enhance its effectiveness and accelerate its absorption. This study aimed to explore the therapeutic potential of propolis nanoparticles in the treatment of diabetic ulcers in a streptozotocin-induced type I diabetic rat model. Male Wistar rats with diabetic ulcers were treated topically with propolis nanoparticles for 14 days, and outcomes were assessed based on wound closure rate, histological characteristics, and oxidative stress markers. Wound closure was measured on days 7 and 14 post injury. Histological analysis focused on epidermal thickness and subcutaneous tissue formation, whereas oxidative stress was assessed by serum malondialdehyde (MDA) levels at baseline, day 1, and day 7. The results showed that propolis nanoparticles accelerated wound closure by days 7 (P < 0.05) and 14 (P > 0.05). Histologically, the treated wounds exhibited improved structural restoration, with hair follicles and sebaceous glands. The treated wounds also had a thinner epidermis, indicating controlled proliferation and a reduced risk of abnormal scar formation. MDA levels were lower in the propolis-nanoparticle-treated group than in the untreated group (P > 0.05). Propolis nanoparticles demonstrated potential in promoting early-stage wound healing in diabetic rats, suggesting they could be a valuable addition to the therapeutic options for diabetic ulcer management.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
Spampinato SF, Caruso GI, De Pasquale R, Sortino MA, Merlo S. The treatment of impaired wound healing in diabetes: Looking among old drugs. Pharmaceuticals. 2020; 13(4): 60.
World Health Organization. The top 10 causes of death [Online]. 2020 [cited 2023 Jul 4]. Available from: [https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death](https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death).
IDF Diabetes Atlas. Indonesia diabetes report 2000–2045 [Online]. 2023 [cited 2023 Jul 24]. Available from: [https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/country/94/id.html](https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/country/94/id.html).
American Diabetes Association. 2. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care. 2021; 44(Suppl. 1): S15–33.
Oliver T, Mutluoglu M. Diabetic foot ulcer [Online]. 2022 [cited 2023 Jul 4]. Available from: [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537328](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537328).
Edmonds M, Manu C, Vas P. The current burden of diabetic foot disease. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2021; 17: 88–93.
Ojo BO, Enwuru NV, Mendie UE. Evaluation of honey-based pharmaceutical preparations for the management of diabetic wounds. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2022; 6(1): 109–116.
Dasari N, Jiang A, Skochdopole A, Chung J, Reece EM, Vorstenbosch J, Winocour S. Healing, inflammation, and fibrosis: updates in diabetic wound healing, inflammation, and scarring. Semin Plast Surg. 2021; 35(3): 153.
Holzer-Geissler JCJ, Schwingenschuh S, Zacharias M, Einsiedler J, Kainz S, Reisenegger P, Holecek C, Hofmann E, Wolff-Winiski B, Fahrngruber H, Birngruber T, Kamolz LP, Kotzbeck P. The impact of prolonged inflammation on wound healing. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4): 856.
Worsley AL, Lui DH, Ntow-Boahene W, Song W, Good L, Tsui J. The importance of inflammation control for the treatment of chronic diabetic wounds. Int Wound J. 2023; 20(6): 2346–2359.
Herman A, Herman AP. Herbal products and their active constituents for diabetic wound healing—preclinical and clinical studies: a systematic review. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(1): 281.
Sam S. Importance and effectiveness of herbal medicines. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2019; 8(2): 354–357.
Nimesh S, Ashwlayan VD, Rani R, Prakash O. Advantages of herbal over allopathic medicine in the management of kidney and urinary stones disease. Borneo J Pharm. 2020; 3(3): 179–189.
Sforcin JM. Biological properties and therapeutic applications of propolis. Phytother Res. 2016; 30(6): 894–905.
Abdullah NA, Zullkiflee N, Zaini SNZ, Taha H, Hashim F, Usman A. Phytochemicals, mineral contents, antioxidants, and antimicrobial activities of propolis produced by Brunei stingless bees Geniotrigona thoracica, Heterotrigona itama, and Tetrigona binghami. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2020; 27(11): 2902–2911.
Kahono S, Chantawannakul P, Engel MS. Social bees and the current status of beekeeping in Indonesia. Asian Beekeeping in the 21st Century; 2018. 287–306 p.
Samsudin SF, Mamat MR, Hazmi IR. Taxonomic study on selected species of stingless bee (hymenoptera: apidae: meliponini) in peninsular Malaysia. Serangga. 2018; 23(2): 203–258.
Purwanto H, Soesilohadi RCH, Trianto M. Stingless bees from meliponiculture in South Kalimantan, Indonesia. Biodiversitas. 2022; 23(3): 1254–1266.
Lee S, Duwal RK, Lee W. Diversity of stingless bees (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Meliponini) from Cambodia and Laos. J Asia Pac Entomol. 2016; 19(4): 947–961.
Abduh MY, Adam A, Fadhlullah M, Putra RE, Manurung R. Production of propolis and honey from Tetragonula laeviceps cultivated in modular Tetragonula hives. Heliyon. 2020; 6(11): e05405.
Pazin WM, Mônaco L da M, Egea Soares AE, Miguel FG, Berretta AA, Ito AS. Antioxidant activities of three stingless bee propolis and green propolis types. J Apic Res. 2017; 56(1): 40–49.
Liu E, Gao H, Zhao YJ, Pang Y, Yao Y, Yang Z, Zhang X, Wang Y, Yang S, Ma X, Zeng J, Guo J. The potential application of natural products in cutaneous wound healing: A review of preclinical evidence. Front Pharmacol. 2022; 13: 900439.
Suhandi C, Wilar G, Lesmana R, Zulhendri F, Suharyani I, Hasan N, Wathoni N. Propolis-based nanostructured lipid carriers for α-mangostin delivery: formulation, characterization, and in vitro antioxidant activity evaluation. Molecules. 2023; 28(16): 6057.
Gvazava IG, Kosykh AV, Rogovaya OS, Popova OP, Sobyanin KA, Khrushchev AK, Timofeev AV, Vorotelyak EA. A simplified streptozotocin-induced diabetes model in nude mice. Acta Naturae. 2020; 12(4): 98–104.
Gonzalez DH, Paulson SE. Quantification of malondialdehyde in atmospheric aerosols: application of the thiobarbituric acid method. Aerosol Air Qual Res. 2022; 22(7): 220037.
Tang Q, Su YW, Xian CJ. Determining oxidative damage by lipid peroxidation assay in rat serum. Bio Protoc. 2019; 9(12): e3263.
Bigliardi P, Langer S, Cruz JJ, Kim SW, Nair H, Srisawasdi G. An Asian perspective on povidone iodine in wound healing. Dermatology. 2017; 233(2–3): 223–233.
Niri R, Hassan D, Lucas Y, Treuillet S. A superpixel-wise fully convolutional neural network approach for diabetic foot ulcer tissue classification. In: Pattern recognition icpr international workshops and challenges; 2021. 308–320 p.
Vestweber PK, Wächter J, Planz V, Jung N, Windbergs M. The interplay of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus in dual-species biofilms impacts development, antibiotic resistance and virulence of biofilms in in vitro wound infection models. PLoS One. 2024; 19(5): e0304491.
Ibrahim N, Zakaria AJ, Ismail Z, Mohd KS. Antibacterial and phenolic content of propolis produced by two Malaysian stingless bees, Heterotrigona itama and Geniotrigona thoracica. Int J Pharmacogn Phytochem Res. 2016; 8(1): 156–161.
El-Sakhawy M, Salama A, Tohamy HAS. Applications of propolis-based materials in wound healing. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024; 316(1): 1–13.
Kucharzewski M, Kózka M, Urbanek T. Topical treatment of nonhealing venous leg ulcer with propolis ointment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013: 254017.
Mujica V, Orrego R, Fuentealba R, Leiva E, Zúñiga-Hernández J. Propolis as an adjuvant in the healing of human diabetic foot wounds receiving care in the diagnostic and treatment centre from the regional hospital of Talca. J Diabetes Res. 2019; 2019: 2507578.
Witjaksana A, Widjiastuti I, Juniarti D. Effective dose of nano propolis as anti-pain in animal models of Mus Musculus using writhing test method. Conservative Dentistry Journal. 2023; 13: 7–10.
Conceição M, Gushiken LFS, Aldana-Mejía JA, Tanimoto MH, Ferreira MV de S, Alves ACM, Miyashita MN, Bastos JK, Beserra FP, Pellizzon CH. Histological, immunohistochemical and antioxidant analysis of skin wound healing influenced by the topical application of Brazilian red propolis. Antioxidants. 2022; 11(11): 2188.
Mony MP, Harmon KA, Hess R, Dorafshar AH, Shafikhani SH. An updated review of hypertrophic scarring. Cells. 2023; 12(5): 678.
Loo HL, Goh BH, Lee LH, Chuah LH. Application of chitosan-based nanoparticles in skin wound healing. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2022; 17(3): 299–332.
Yang J, He Y, Nan S, Li J, Pi A, Yan L, Xu J, Hao Y. Therapeutic effect of propolis nanoparticles on wound healing. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2023; 82: 104284.
Nuutila K. Hair Follicle Transplantation for wound repair. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2021; 10(3): 153.
Veniaminova NA, Jia YY, Hartigan AM, Huyge TJ, Tsai SY, Grachtchouk M, Nakagawa S, Dlugosz AA, Atwood SX, Wong SY. Distinct mechanisms for sebaceous gland self-renewal and regeneration provide durability in response to injury. Cell Rep. 2023; 42(9): 113121.
Tamara A, Oktiani BW, Taufiqurrahman I. The effect of flavonoid extract of Kelulut propolis (G. thoracica) on the number of neutrophil cells in periodontitis (in vivo study on male Wistar rats). Dentin. 2019; 3(1): 10–16.
Ling T, Boyd L, Rivas F. Triterpenoids as reactive oxygen species modulators of cell fate. Chem Res Toxicol. 2022; 35(4): 569.
Kindler S, Schuster M, Seebauer C, Rutkowski R, Hauschild A, Podmelle F, Metelmann C, Metelmann B, Müller-Debus C, Metelmann HR, Metelmann I. Triterpenes for well-balanced scar formation in superficial wounds. Molecules. 2016; 21(9): 1129.
Caturano A, D’Angelo M, Mormone A, Russo V, Mollica MP, Salvatore T, Galiero R, Rinaldi L, Vetrano E, Marfella R, Monda M, Giordano A, Sasso FC. Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: impacts from pathogenesis to lifestyle modifications. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023; 45(8): 6651–6666.
Wang G, Yang F, Zhou W, Xiao N, Luo M, Tang Z. The initiation of oxidative stress and therapeutic strategies in wound healing. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023; 157: 114004.
Jakubczyk K, Dec K, Kałduńska J, Kawczuga D, Kochman J, Janda K. Reactive oxygen species - sources, functions, oxidative damage. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2020; 48(284): 124–127.
Dayem AA, Hossain MK, Lee S Bin, Kim K, Saha SK, Yang GM, Choi HY, Cho SG. The role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the biological activities of metallic nanoparticles. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18(1): 120.
Bardaweel SK, Gul M, Alzweiri M, Ishaqat A, Alsalamat HA, Bashatwah RM. Reactive oxygen species: The dual role in physiological and pathological conditions of the human body. Eurasian J Med. 2018; 50(3): 193–201.
Li YR, Jia Z, Trush MA. Defining ROS in biology and medicine. React Oxyg Species (Apex). 2016; 1(1): 9–21.
Biswas SK. Does the interdependence between oxidative stress and inflammation explain the antioxidant paradox? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016: 5698931.
Sylviana N, Gunawan H, Lesmana R, Purba A, Akbar IB. Effects of astaxanthin and regular exercise on oxidative stress patterns in men after strenuous activity. Indones J Clin Pharm. 2017; 6(1): 46–54.
Orlowski P, Zmigrodzka M, Tomaszewska E, Ranoszek-Soliwoda K, Czupryn M, Antos-Bielska M, Szemraj J, Celichowski G, Grobelny J, Krzyzowska M. Tannic acid-modified silver nanoparticles for wound healing: the importance of size. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018; 13: 991–1007.
Meida NS, Purwanto B, Wasita B, Indrakila S, Soetrisno S, Poncorini E, Cilmiaty R, Pratiwi WR, Setyandriana Y, Almahira S. Effect of propolis extract on oxidative stress biomarker in diabetic Wistar rat (Rattus norvegicus). Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2022; 6(8): 1193–1196.
Mayasari CK, Dwirini RG, Octovia LI. Potential role of propolis flavonoid on malondialdehyde and superoxide dismutase levels on endometriosis. J La Medihealtico. 2024; 5(2): 323–339.
Megantara I, Murad C, Pahlevi F, Sylviana N, Goenawan H, Lesmana R. The effect of propolis extract from Sumatra, Indonesia on Escherichia coli and IL-6 gene expression in male Wistar rats fed with a high-fat diet. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2024; 8(6): 7350–7354.
Tyastono RDN, Sungkar A, Yarsa KY, Haryanti D, Agustrina N, Budi IB, Wasita B. Difference of propolis administration as an antioxidant against oxidative stress (Malondialdehyde level (MDA)) and apoptosis (caspase-3 expression) in skin graft model white rats (Rattus norvegicus). Asian J Surg. 2021; 5(7): 1–7.