The Neuroprotective Potential of Anacardium occidentale (Cashew) Seed Extract Against BPA-Induced Neurotoxicity in Male Wistar Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
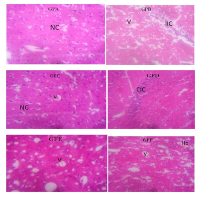
Bisphenol A (BPA), an environmental toxin, disrupts neural development and function in the cerebral cortex by inducing oxidative stress and inflammation. This study investigated the neuroprotective potential of Anacardium occidentale (cashew) seed extract against Bisphenol A (BPA)-induced neurotoxicity in male Wistar rats. Thirty six rats were separated into six groups: control (A), BPA-treated (B, 50 mg/kg), cashew-only (C, 600 mg/kg), and BPA-treated groups with extract (D, 150 mg/kg), extract (E, 300 mg/kg), or extract(F, 600 mg/kg) treatment. Body weight, neurobehavioral indices (as assessed by the open-field test), and histological analysis of the cerebral cortex were evaluated over a 28-day period. Group B (BPA exposure) significantly reduced weight gain (194.00 ± 11.77 g vs. control: 183.50 ± 16.26 g, p*<0.0001), suppressed exploratory activity (line crossing: 26.00 ± 10.61s vs. 40.00 ± 24.04s), and increased anxiety-like behavior (2.12 ± 1.41s vs. 1.36 ± 1.43s). Extensive neuronal degeneration, vacuolation, and inflammation were observed histologically in Group B. Anacardium occidentale extract, particularly at 600 mg/kg, reversed these changes: Group F (600 mg/kg) resumed exploratory activity (26.00 ± 9.31s line crossing) and reduced freezing (1.00 ± 1.27s), near to control. Histological changes included moderate neuroregeneration and reduced inflammation, with high-dose cashew (F) showing nearly normal neuronal architecture. Lower doses (150 mg/kg, 300 mg/kg) improved weight gain but were less effective in behavioral effects. The findings indicate that Anacardium occidentale seed extract, particularly at higher doses, reverses cerebral toxicity induced by BPA, suggesting its potential as a natural agent against environmental neurotoxicants.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1.Hyun SA, Ka M. Bisphenol A (BPA) and neurological disorders: An overview. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2024;173:106614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2024.106614.
2.Lee CY, Hyun SA, Ko MY, Kim HR, Rho J, Kim KK, Kim WY, Ka M. Maternal Bisphenol A (BPA) exposure alters cerebral cortical morphogenesis and synaptic function in mice. Cereb Cortex. 2021;31(12):5598–5612. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhab183.
3.Hyun SA, Ko MY, Jang S, Lee BS, Rho J, Kim KK, Kim WY, Ka M. Bisphenol-A impairs synaptic formation and function by RGS4-mediated regulation of BDNF signaling in the cerebral cortex. Dis Model Mech. 2022;15(7):dmm049177. https://doi.org/10.1242/dmm.049177.
4.Mustieles V, Fernández MF. Bisphenol A shapes children's brain and behavior: Towards an integrated neurotoxicity assessment including human data. Environ Health. 2020;19(1):66. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12940-020-00620-y.
5.Schirmer E, Schuster S, Machnik P. Bisphenols exert detrimental effects on neuronal signaling in mature vertebrate brains. Commun Biol. 2021;4(1):465. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-01966-w.
6.Baptista AB, Sarandy MM, Gonçalves RV, Novaes RD, Gonçalves da Costa C, Leite JP, Peluzio MD. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of Anacardiumoccidentale L. and Anacardiummicrocarpum D. extract on the liver of IL-10 knockout mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:3054521. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3054521.
7.Iwuanyanwu VU, Banjo OW, Babalola KT, Olajide OA. Neuroprotection by Alstoniaboonei De Wild., Anacardiumoccidentale L., AzadirachtaindicaA.Juss. and Mangiferaindica L. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023;310:116390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.116390.
8.Fabrello J, Ciscato M, Munari M, Vecchiatti A, Roverso M, Bogialli S, MatozzoV.Ecotoxicological effects and bioaccumulation of BPA analogues and their mixture in the clam Ruditapesphilippinarum. Mar Environ Res. 2023;192:106228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marenvres.2023.106228.
9.Banerjee O, Singh S, Paul T, Maji BK, Mukherjee S. Centellaasiatica mitigates the detrimental effects of Bisphenol-A (BPA) on pancreatic islets. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):8043. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-58545-2.
10.Salehi B, Gültekin-Özgüven M, Kirkin C, Özçelik B, Morais-Braga MFB, Carneiro JNP, et al. Antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anticancer effects of Anacardium plants: An ethnopharmacological perspective. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:295 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00295.
11.Siracusa R, Fusco R, Peritore AF, Cordaro M, D’Amico R, Genovese T, Gugliandolo E, Crupi R, Smeriglio A, Mandalari G, CuzzocreaS.The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Anacardiumoccidentale L. cashew nuts in a mouse model of colitis. Nutrients. 2020;12(3):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12030834.
12.Gaitán-Jiménez SY, Restrepo-Sánchez LP, Parada-Alfonso F, Narváez-Cuenca CE. Cashew (Anacardiumoccidentale) nut-shell liquid as an antioxidant in bulk soybean oil. Molecules. 2022;27(24):8733. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules27248733.
13.Duangjan C, Rangsinth P, Zhang S, Wink M, Tencomnao T. Anacardiumoccidentale L. leaf extracts protect against glutamate/H₂O₂-induced oxidative toxicity and induce neurite outgrowth: The involvement of SIRT1/Nrf2 signaling pathway and teneurin 4 transmembrane protein. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:627738. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.627738.
14.Inwang UA, Ukaegbu KC, Onyagu LU, Uchewa OO, Ogbonna ID. Synergistic effect of ethanol extract of Anacardiumoccidentale leaves and Musa sapientum peels on fine motor function against cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2025;16(3):733–740. https://doi.org/10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.16(3).733-40.
15.Oyagbemi AA, Adebayo AK, Adebiyi OE, Adigun KO, Folarin OR, Esan OO, Ajibade TO, Ogunpolu BS, Falayi OO, Ogunmiluyi IO, OlutayoOmobowaleT.Leaf extract of Anacardiumoccidentale ameliorates biomarkers of neuroinflammation, memory loss, and neurobehavioral deficit in L-NAME-treated rats. Biomarkers. 2023;28(3):263–272. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2022.2164354.
16.Désiré GN, Simplice FH, Guillaume CW, Kamal FZ, Parfait B, Hermann TD, Hervé NA, Eglantine KW, Linda DK, Roland RN, Balbine KN. Cashew (Anacardiumoccidentale) extract: Possible effects on hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in modulating chronic stress. Brain Sci. 2023;13(11):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13111561.
17.Aisha Aminu AA, HauwaOnozasi Umar HO, Wusa Makena WM, ZakariaAlhaji Isa ZA, Muhammad Goni ZM, Bethel Onimisi OB, BarkaIshaku BI. Antagonistic effectiveness of Anacardiumoccidentale leaf extract on lead-acetate exposure-induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Environ Anal Health Toxicol. 2023;38(4):e2023028-0. https://doi.org/10.5620/eaht.2023028.
18.Linillos-Pradillo B, Rancan L, Paredes SD, Schlumpf M, Lichtensteiger W, Vara E, TresguerresJÁ.Low-dose of BPA induces liver injury through oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in Long-Evans lactating rats and its perinatal effect on female PND6 offspring. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4585. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24054585.
19.Manzoor MF, Tariq T, Fatima B, Sahar A, Tariq F, Munir S, Khan S, Nawaz Ranjha MM, Sameen A, Zeng XA, Ibrahim SA. An insight into bisphenol A, food exposure and its adverse effects on health: A review. Front Nutr. 2022;9:1047827. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.1047827.
20.Gerona RR, Woodruff TJ, Dickenson CA, Pan J, Schwartz JM, Sen S, et al. Bisphenol-A (BPA), BPA glucuronide, and BPA sulfate in midgestation umbilical cord serum in a northern and central California population. Environ Sci Technol. 2013;47(21):12477–12485. https://doi.org/10.1021/es402764d.
21.Caldas APS, Rocha DMUP, Dionísio AP, Hermsdorff HHM, Bressan J. Brazil and cashew nuts intake improve body composition and endothelial health in women at
cardiometabolic risk (Brazilian Nuts Study): A randomized controlled trial. Br J Nutr. 2022;1–38. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711452100475X.
22.Gonçalves B, Pinto T, Aires A, Morais MC, Bacelar E, Anjos R, Ferreira-Cardoso J, Oliveira I, Vilela A, Cosme F. Composition of nuts and their potential health benefits—An overview. Foods. 2023;12(5):942. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12050942.
23.Chen Y, Xu HS, Guo TL. Modulation of cytokine/chemokine production in human macrophages by bisphenol A: A comparison to analog and interactions with genistein. J Immunotoxicol. 2018;15(1):96–103. https://doi.org/10.1080/1547691X.2018.1476629.
24.Perera F, Nolte EL, Wang Y, Margolis AE, Calafat AM, Wang S, Garcia W, Hoepner LA, Peterson BS, Rauh V, HerbstmanJ.Bisphenol A exposure and symptoms of anxiety and depression among inner-city children at 10–12 years of age. Environ Res. 2016;151:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2016.07.028.
25.Ni Y, Hu L, Yang S, Ni L, Ma L, Zhao Y, Zheng A, Jin Y, Fu Z.Bisphenol A impairs cognitive function and 5-HT metabolism in adult male mice by modulating the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Chemosphere. 2021;282:130952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.130952.
26.Zhang H, Wang Z, Meng L, Kuang H, Liu J, Lv X, Pang Q, Fan R. Maternal exposure to environmental bisphenol A impairs the neurons in the hippocampus across generations. Toxicology. 2020;432:152393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2020.152393.
27.Akomolafe SF, Asowata-Ayodele AM. Roasted cashew (Anacardiumoccidentale L.) nut-enhanced diet forestalls cisplatin-initiated brain harm in rats. Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e11066. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11066.
28.Seibenhener ML, Wooten MC. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J Vis Exp. 2015;(96):52434.
29.Inwang UA, Agha JN, Etti IC, Nwuzor EO, Udu PO. Ethanol extract of Anacardiumoccidentale leaves and Musa sapientum peels co-treatment enhanced cognitive and olfactory functions via antioxidant mechanism in cadmium-induced brain damage in female Wistar rats. Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2025; 9(5):2907–2913. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i6.75
30.Inwang UA, Ogwo EU. Polyherbal formulation enhanced sensorimotor function in oxidative stress induced by unpredicted mild chronic stress in Wistar rats. Arch Razi Inst. 2025 May 31.
31.Odu PO, Ujah GA, Uket JM, Odu VK, Inwang UA. Costusafer leaves extract ameliorates stress-induced alterations in hematological and lipid parameters in Wistar rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2025;9(6):2821–2826. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i6.63
32.Iheanacho CM, Akubuiro PC, Oseghale IO, Imieje VO, Erharuyi O, Ogbeide KO, Jideonwo AN, Falodun A. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of the stem bark extracts of Anacardiumoccidentale (Linn) Anacardiaceae. Trop J Phytochem Pharm Sci. 2023 May 1;2(2):65–69. http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjpps/v2i2.4
33.Inwang UA, Ben EE, Uchewa OO, Nwuzor EO, Nwaji AR, Umoh EA. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Talinumtriangulare methanol leaf extract on cadmium-induced cognitive dysfunction in male Wistar rats. Nat Prod Commun. 2024;19(8):1934578X241271698.
34.Etti I. Neuroprotective effect of Andrographispaniculata (Burm. f.) leaf extract in aluminum chloride-induced Alzheimer's disease in mice. J Curr Biomed Res. 2024;4(3):1618–1627.
35.Koofreh D, Nsikak U, Edet A, Inwang U. Ethanol leaf-extract of Moringaoleifera protect against hyperglycaemic-induced neuronal impairment in albino Wistar rats.Eur J Biomed. 2020;7(7):50–60.
36.Inwang UA, Davies KG, Ekong MB, Obasi CP, Onyebuenyi M, Nwaji AR. The anti-oxidative and cognitive properties of Zingiberofficinale rhizome ethanol extract and its dichloromethane and n-hexane fractions against aluminium chloride-induced neurotoxicity in swiss mice.Int J Pharm Sci Res. 2023;14(3):1196–201.