Curcuma longa Extract Attenuates Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Neurotoxicity in the Cerebral Cortex of Wistar Rats: Evidence for Neuroprotective Effect
Main Article Content
Abstract
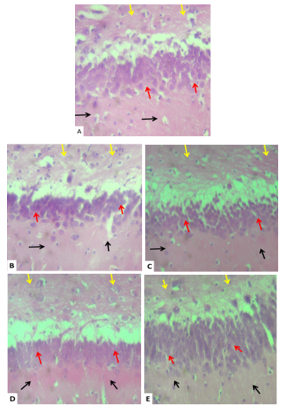
Curcuma longa, commonly known as turmeric, has been traditionally used for various medicinal purposes, including the treatment of neurological disorders. The present study aimed to investigate the neuroprotective effects of Curcuma longa (turmeric) on pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Thirty-five (35) Wistar rats were divided into five groups (n =7), and treated as follows; Group A received distilled water (control), Group B received 35 mg/kg of PTZ and DZP (diazepam), Group C received PTZ intraperitoneally to induce epilepsy, Group D received 250 mg/kg of C. longa with 35 mg/kg of PTZ, and Group E received 500 mg/kg of C. longa with 35 mg/kg of PTZ. The extract was administered once daily for 28 days, during which period seizure severity and frequency were assessed. At the end of the treatment period, the levels of antioxidant enzyme glutathione (GSH), and oxidative stress biomarker malondialdehyde (MDA) were measured. The results revealed that PTZ administration significantly increased seizure severity, and increased oxidative stress by decreasing GSH concentration and increasing MDA level in the cerebral cortex. Treatment with C. longa extract at 250 mg/kg and 500 mg/kg exhibit anticonvulsant effect by reducing seizure severity in PTZ-induced Wistar rats. In addition, C. longa extract reduced oxidative stress and improved neuroprotection by significantly (P < 0.05) increasing GSH level, and decreasing MDA level in the cerebral tissues of PTZ-induced Wistar rats. These findings indicate that C. longa extract has neuroprotective effects and anticonvulsant properties, making it a promising candidate for adjunctive therapy in epilepsy management.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1. Stafstrom CE and Carmant L. Seizures and Epilepsy: An Overview for Neuroscientists. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015; 5(6):a022426. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022426
2. World Health Organization, International League Against Epilepsy, International Bureau for Epilepsy. Epilepsy: A Public Health Imperative [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019 [cited 2025:5:4]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/epilepsy-a-public-health-imperative
3. Hassan LA, Anyanwu GE, Nto JN, Abireh IE, Akunna GG. Protective Effect of Aqueous Extract of Cyperus esculentus on Flutamide-Induced Testicular Defect of Male Wistar Rats. Sch J Appl Med Sci. 2018; 6(6):2391-2395.
4. Hassan LA, Anyanwu GE, Jacks T, Esom E, Ojo FO, Muhammed BM. Alkaloid Fraction of Cyperus esculentus Tubers Reversed Lead-Induced Cerebral Toxicity Via Modulation of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers. Acta Bioscientia. 2025; 1(2):00-00. DOI: https://doi.org/10.71181/actabioscientia12250
5. Wang Y, Wang X, Zhang J, Li H, Zhang Y, Yu J. Efficacy of Curcumin on Aortic Atherosclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in Mouse Models. Biomed Res Int. 2020; 2020:5172051.
6. Zagórska J, Kukula-Koch W, Czop M, Iłowiecka K, Koch W. Impact of Thermal Processing on the Composition of Curcuma longa Rhizome. Foods. 2023; 12:3086. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12163086
7. Pothitirat W and Gritsanapan W. Variability of Curcuminoids: Antioxidative Components in Ethanolic Turmeric Extract Determined by UV and HPLC Methods. Acta Hort (ISHS). 2008; 786:175-184. DOI: https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2008.786.19
8. Zeng L, Yang T, Yang K, Yu G, Li J, Xiang W, Chen H. Efficacy and Safety of Curcumin and Curcuma longa Extract in the Treatment of Arthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:891822. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.891822
9. Wright J, Pickard N, Whitfield A, Hakin N. A Population-Based Study of the Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics and Effect of Ethnicity in Epilepsy. Seizure. 2000; 9(5):309-313. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1053/seiz.2000.0422
10. Grewal GK, Kukal S, Kanojia N, Saso L, Kukreti S, Kukreti R. Effect of Oxidative Stress on ABC Transporters: Contribution to Epilepsy Pharmacoresistance. Molecules. 2017; 22(3):365. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22030365
11. Pahuja M, Mehla J, Reeta KH, Joshi SD, Gupta YK. Effect of Nimodipine on the Development of Kindling and Associated Cognitive Dysfunction in Rats. Epilepsy Behav. 2013; 27(2):206-211.
12. Zhen Y, Liu J, Wang Y, Chen X, Zhang H. Sodium Selenate Retards Epileptogenesis in Acquired Epilepsy Models Through PP2A Activation. Brain. 2016; 139(6):1629-1632.
13. Shimada T and Yamagata K. Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Kindling Mouse Model. J Vis Exp. 2018; (136):e56573. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3791/56573-v
14. Méndez-Cuesta LA, Márquez B, Cruz VP, Escobar-Briones C, Galvan S, Alvarez-Ruiz Y, Maldonado PD, Santana R, Santamaría A, Carrillo-Mora P. Diazepam Blocks Striatal Lipid Peroxidation and Improves Stereotyped Activity in a Rat Model of Acute Stress. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2011; 109:350-356. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00738.x
15. Kumar P, Kumar V, Mahapatra SK. Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.): A Review of Its Medicinal Properties. J Ayurveda Integr Med. 2018; 9(3):157-165.
16. Buba HS, Bello AM, Makena W, Garba SH, Hassan LA, Ojo FO, Jajere FB. Neuroprotective Effects of Curcuma longa on Pentylenetetrazole-Induced Neurotoxicity on Hippocampus of Albino Wistar Rats. Afr J Biomed Res. 2025; 8(2):13-24. DOI: https://doi.org/10.52589/AJBMR-CFMVGORV