The Effect of a High-Whey Protein Diet Combined With Lactobacillus acidophilus on Insulin Resistance, Intestinal Microbiota, and the Histology of the Liver, Spleen, Kidneys, and Colon
Main Article Content
Abstract
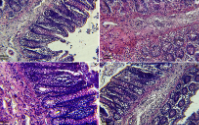
The diet profoundly impacts the microbial ecology in the gastrointestinal tract and the majority of biological functions. This study attempts to discover the effects of chronic high-protein diets (HPD) and Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) on the liver, spleen, kidneys, and colon histology, with a special focus on their interactions with the gut flora. In a 12-week treatment program, which categorised four groups of obese rats, each receiving either a normal diet (14% whey protein) or a high-protein diet (50% whey protein), with and without the inclusion of Lactobacillus acidophilus (LAB). The HPD diet significantly increased liver transaminases (AST (78.29 U/L) and ALT (66.43 U/L)), while normal diets raised insulin levels (0.95 µU/mL); however, their combination with LAB improved HbA1c (2.5) and insulin levels (0.25µU/mL). HPD caused infiltrations in the muscular layers of the colon and hypertrophy of the glomeruli, as well as dilation and congestion of the capillary sinuses, not to mention the significant infiltration in the splenic red and white pulps. Normal diets caused fatty deposits in the kidneys and hyalinisation of the tubules, as well as lymphatic aggregations in the intestinal crypts and damage to epithelial tissue. The consumption of high-protein diets in association with LAB (10%) significantly increased the number of Lactobacillus compared to the group on normal diets and Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 in HPD without LAB association (12%). The association of LAB to
the HPD diet improves their impact on general physiological functions and specifically improves gut microbiota.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1. Desoky AMAA. The Potential Histological Effect of Experimental Obesity on The Liver of Male Albino Rats (Light and Electron Microscopic Study). Egypt J Hosp Med. 2022;89(1):5028–5039.
2. Kratz M, Baars T, Guyenet S. The relationship between highfat dairy consumption and obesity, cardiovascular, and metabolic disease. Eur. J.Nutr. 2013;52(1):1-24.
3. Díaz-Rúa R, Keijer J, Palou A, van Schothorst EM, Oliver P. Long-term intake of a high-protein diet increases liver triacylglycerol deposition pathways and hepatic signs of injury in rats. J Nutr Biochem. 2017;46:39–48.
4. Speretta GF, Leite RD, Duarte ACDO. Obesidade, inflamação e exercício: foco sobre o TNF-α e IL-10. Rev Hosp Univ Pedro Ernesto. 2014;13:61–69. https://doi.org/10.12957/rhupe.2014.9807 .
5. Ley EJ, Singer MB, Clond MA, Johnson T, Bukur M, Chung R, Margulies DR, Salim A. Long-term effect of trauma splenectomy on blood glucose. J Surg Res. 2012;177:152–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jss.2012.03.068.
6. Wakefield AP, House JD, Ogborn MR, Weiler HA, Aukema HM. A diet with 35% of energy from protein leads to kidney damage in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Br J Nutr. 2011;106:656–663. Doi: 10.1017/S0007114511000730.
7. Gurgen SG, Yucel AT, Karakus AC, Cecen D, Ozen G, Kocturk S. Usage of whey protein may cause liver damage via inflammatory and apoptotic responses. Hum Exp Toxicol.2014;28:1–11. doi: 10.1177/0960327114556787.
8. Pontes TC, Fernandes FGM, Trindade AS, Sobral Filho JF. Incidence of acne vulgaris in young adult users of proteincalorie supplements in the city of João Pessoa – PB. An Bras Dermatol.2013;88:907–912. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20132024.
9. Moreno-Pérez D, Bressa C, Bailén M, Hamed-Bousdar S, Naclerio F, Carmona M, Pérez M, González-Soltero R, Montalvo-Lominchar MG, Carabaña C, Larrosa M. Effect of a protein supplement on the gut microbiota of endurance athletes: A randomised, controlled, double-blind pilot study. Nutrients. 2018;10:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10030337.
10. Siddiq A, Osibemhe M, Nura L, Maibulangu B. M. Cardioand-Hepatoprotective Benefits of Some Spices in Wistar Rats Induced with Metabolic Syndrome. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2022;6:1707–1714.
11. Aparicio VA, Nebot E, Porres JM., Ortega FB, Heredia JM, Lopez-Jurado M, Ramirez PA. Effects of high-whey-protein intake and resistance training on renal, bone and metabolic parameters in rats. Br J Nutr. 2011;105:836–845. Doi: 10.1017/S0007114510004393.
12. Eaimworawuthikul S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Suntornsaratoon P. Altered gut microbiota ameliorates bone pathology in the mandible of obese – insulin-resistant rats. Eur.J.Nutr.2020;59:1453–1462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-019-02002-8
13. Griffin JWD, Bradshaw PC. Effects of a high protein diet and liver disease in an in silico model of human ammonia metabolism. Theor Biol Med Model. 2019;16:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12976-019-0109-1.
14. Adebolu TT, Adediwura D V., Aiyenuro EA. Antibacterial Activity of Sorghum “Ogi” on Diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli. J Adv Microbiol. 2018;12:1–8. https://doi.org/10.9734/jamb/2018/44011.
15. Waynforth HB and Flecknell PA. Experimental and Surgical Technique in the Rat Second Edition Elsevier book 2014; Second Edi:1–377.
16. Belkacem S, Bammoune A, Bali MM, Yargui L. Evaluation of insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetics. Alg J Med Heal Res. 2022;1:61–74.
17. Liu J, Gu Z, Song F, Zhang H, Zhao J, Chen W. Lactobacillus plantarum ZS2058, and Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Use different mechanisms to prevent Salmonella infection in vivo. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:1–9.
18. Serra F, Bonet L, Palou A. Amino-acid-enzyme activities in brown and white adipose tissues and the liver of cafeteria rats. Effects of 24 hours starving. Arch Int Physiol Biochim.1987;95:263–268
19. Reis CEG. Discussion of “Whey protein supplementation and its potentially adverse effects on health: a systematic review”—Unsubstantiated claims of adverse effects of whey protein supplementation on human kidney and liver function. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2021; 46(1):90–91.
https://doi.org/10.1139/ apnm-2020-0674 PMID: 33399522
20. Abd El-Aziz R, Naguib M, Rashed LA. Spleen size in patients with metabolic syndrome and its relation to metabolic and inflammatory parameters. Egypt J Intern Med. 2018;30:78–82. https://doi.org/10.4103/ejim.ejim_86_17.
21. Gallagher D, Kelley DE, Thornton J, Boxt L, Pi-Sunyer X, Lipkin E, et al. MRI Ancillary Study Group of the Look AHEAD Research Group. Changes in skeletal muscle and organ size after a weight-loss intervention in overweight and obese type 2 diabetic patients. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017; 105:78–
84.
22. Madsen L, Myrmel LS, Fjære E, Liaset B, Kristiansen K, Madsen L. Links between Dietary Protein Sources, the Gut Microbiota, and Obesity. Front. physiol. 2017;8:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.01047.
23. de Souza TA, de Souza DW, Siqueira BS, Rentz T, de Oliveria Emílio HR, Grassiolli S. Splenic participation in glycemic homeostasis in obese and non-obese male rats. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2020;14:479–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2020.07.009.
24. Santana ES dos S, de Oliveira CA, Lima FIA, Nucci RAB, Fonseca FLA, Maifrino LBM. Effect of Resistance Training and Diet Intake on Spleen Structure of Ovariectomized Wistar Rats. J Heal Allied Sci NU. 2022;12:47–52. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0041-1732812.
25. Rietman A, Schwarz J, Tomé D, Kok FJ, Mensink M. High dietary protein intake, reducing or eliciting insulin resistance? Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014;68:973–979. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2014.123.
26. Aryani HP, Santoso B, Purwanto B, Mudjanarko SW, Utomo B. The Effect of Low-Calorie High Protein Diet on Insulin, TNF-α and P38MAPK levels in insulin-resistant PCOS mice models. Syst Rev Pharm. 2020;11:597–605. https://doi.org/10.31838/srp.2020.10.89.
27. Sun P, Huang L, Shuai P, Wan Z, Liu Yingying, Xue J, Liu Yuping. Effect of a High Protein, Low Glycemic Index Dietary Intervention on Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Front Nutr. 2022;9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2022.863834.
28. Eaimworawuthikul S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Yasom S, Wanchai K. Effects of probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics on jawbone in obese- insulin-resistant rats. Eur J Nutr. 2019;58:2801–2810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-018-1829-4.
29. Newgard, C.B. Interplay between lipids and branched-chain amino acids in the development of insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 2012,15, 606–614.
30. Medeiros CS, Neto IV de S, Silva KKS, Cantuária APC, Rezende TMB, Franco OL, Marqueti R de C, Freitas-Lima LC, Araujo RC, Yildirim A, Mackenzie R, Almeida JA. The effects of high-protein diet and resistance training on glucose control and inflammatory profile of visceral adipose tissue in rats. Nutrients. 2021;6:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13061969.
31. Aparicio VA, Nebot E, Moral RG, Porres JM, Sánchez C. High-protein diets and renal status in rats. Nutr Hosp. 2013;28:232–237.
https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2013.28.1.6165.
32. Yustisia I, Tandiari D, Cangara MH, Hamid F, Daud NA. A high-fat, high-fructose diet-induced hepatic steatosis, renal lesions, dyslipidemia, and hyperuricemia in non-obese rats. Heliyon. 2022;8:e10896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e10896.
33. Tsai CW, Huang HW, Lee YJ, Chen MJ. Investigating the Efficacy of Kidney-Protective Lactobacillus MixtureContaining Pet Treats in Feline Chronic Kidney Disease and Its Possible Mechanism. Animals. 2024;14:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14040630.
34. Lai R, Bian Z, Lin H, Ren J, Zhou H, Guo H. The association between dietary protein intake and colorectal cancer risk : a meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2017:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-017-1241-1.
35. Yu Z, Nan F, Wang LY, Jiang H, Chen W, Jiang Y. Effects of a high-protein diet on glycemic control, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clin Nutr. 2020;39:1724–1734.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2019.08.008.
36. Cui X, Kim E. Dual Effects of High Protein Diet on Mouse Skin and Colonic Inflammation. Clin Nutr Res. 2018;7:56–68.
37. Bingham SA, Pignatelli B, Pollock JR, Ellul A, Malaveille C, Gross G, Runswick S, Cummings JH, O’Neill IK. Does increased endogenous formation of N-nitroso compounds in the human colon explain the association between red meat and colon cancer? J. Carcinog. 1996;17:515-523.
38. Kokou F, Sarropoulou E, Cotou E, Rigos G, Henry M, Alexis M. Effects of fish meal replacement by a soybean protein on growth, histology, selected immune and oxidative status markers of Gilthead Sea bream, Sparus aurata. J World Aquac Soc. 2015;46(2):115–128.
39. Estensoro I, Ballester-Lozano G, Benedito-Palos L, Grammes F, Martos-Sitcha JA, Mydland L-T, et al. Dietary butyrate helps to restore the intestinal status of a marine teleost (Sparus aurata) fed extreme diets low in fish meal and fish oil. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):1–21
40. Beaumont M, Andriamihaja M, Armand L, Grauso M, Jaffrézic F, Laloë D, Moroldo M, Davila A, Tomé D, Blachier F, Lan A. Epithelial response to a high-protein diet in rat colon. BMC Genom. 2017;18:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-017-3514-z.
41. Holmes AJ, Chew YV, Colakoglu F, Cliff JB, Klaassens E, Read MN, Solon-Biet SM, McMahon AC, Cogger VC, Ruohonen K, Raubenheimer D, Le Couteur DG, Simpson SJ. Diet-Microbiome Interactions in Health Are Controlled by Intestinal Nitrogen Source Constraints. Cell Metab.
2017;25:140–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2016.10.021.
42. Reese AT, Pereira FC, Schintlmeister A, Berry D, Wagner M, Hale LP, et al. Microbial nitrogen limitation in the mammalian large intestine. Nat Microbiol. 2018;3:1441–1450. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-018-0267-7.
43. Bartlett A, Kleiner M. Dietary protein and the intestinal microbiota : An understudied relationship. iScience.2022;25:105313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2022.105313.
44. Starke R, Oliphant K, Jehmlich N, Schäpe SS, Sachsenberg T, Kohlbacher O, Allen-Vercoe E, von Bergen M. Tracing incorporation of heavy water into proteins for speciesspecific metabolic activity in complex communities. J Proteomics. 2020;222:1–10.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2020.103791
45. Okediya CK, Oyewale JO, Okediya TT, Ajayi AS, Olasehinde GI. Effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus plantarum on Weight Reduction in Obese Rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2021;5:759–762.
46. Oluwaloni Folusho O, Yakubu Omolara F, Adebayo Abiodun H, Koyejo Oluwatosin D, Lawal Adekunle K. Review of the Gut Microbiota Dynamics in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM): A Focus on Human-Based Studies. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2023;7(6):3059–3079.