Screening Carica Papaya Compounds as an Antimalarial Agent: In Silico Study http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v7i5.9
Main Article Content
Abstract
Malaria is a highly prevalent infectious disease caused by the Plasmodium parasite transmitted through Anopheles mosquitoes, which poses a significant public health challenge worldwide, including in Indonesia. Therefore, a study was conducted to identify potential drug compounds from the Carica papaya plant that could inhibit various antimalarial proteins or receptors, such as Plasmodium falciparum DXR reductase complex with fosmidomycin, Plasmepsin V Plasmodium vivax, P. falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, P. falciparum hexose transporter, P. falciparum protein kinase 5, and P. falciparum dihydrofolate reductase-thymidylate synthase. The
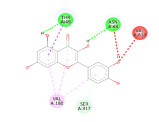
researchers used the Pyrx application to dock the C. papaya compounds with the targeted antimalarial proteins to determine the binding affinity values. Additionally, they used the Yasara dynamics application to conduct molecular dynamics simulation to ensure the stability of the bonds formed between the ligands and proteins. The results showed that 14 compounds found in C. papaya, particularly flavonoids and terpenoids, had the potential to inhibit the six antimalarial proteins with the lowest binding affinity values. Furthermore, the molecular dynamics simulation on 6M20 and 1V0P proteins indicated that the compounds effectively inhibited Plasmodium proteins, as they had an RMSD value below 2.5 Angstrom. The study suggests that C. papaya could be a potential source of antimalarial compounds, which could be developed into new drugs to combat this disease.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Milner DA. Malaria Pathogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2018;8(1):a025569.
Sugiarto SR, Baird JK, Singh B, Elyazar I, Davis TME. The history and current epidemiology of malaria in Kalimantan, Indonesia. Malar J. 2022;21(1):327.
Juhairiyah J, Andiarsa D, Indriyati L, Ridha MR, Prasodjo RS, Dhewantara PW. Spatial analysis of malaria in Kotabaru, South Kalimantan, Indonesia: an evaluation to guide elimination strategies. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2021;115(5):500–11.
Hariono M, Julianus J, Djunarko I, Hidayat I, Adelya L, Indayani F, Auw Z. Namba G, Hariyono P. The Future of Carica papaya Leaf Extract as an Herbal Medicine Product. Mol Basel Switz. 2021;26(22):6922.
Julianti T, De Mieri M, Zimmermann S, Ebrahimi SN, Kaiser M, Neuburger M, Raith M, Brun R, Hamburger M. HPLCbased activity profiling for antiplasmodial compounds in the traditional Indonesian medicinal plant Carica papaya L. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014;155(1):426–34.
Hariono M, Nuwarda RF, Yusuf M, Rollando R, Jenie RI, Al-Najjar B, Julianus J, Putra KC, Nugroho ES, Wisnumurti YK, Dewa SP, Jati BW, Tiara R, Ramadani RD, Qodria L, Wahab HA. Arylamide as Potential Selective Inhibitor for Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9): Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Molecular Modeling. J Chem Inf Model. 2020;60(1):349–59.
Hariono M, Rollando R, Karamoy J, Hariyono P, Atmono M, Djohan M, Wiwy W, Nuwarda R, Kurniawan C, Salin N, Wahab H. Bioguided Fractionation of Local Plants against Matrix Metalloproteinase9 and Its Cytotoxicity against Breast Cancer Cell Models: In Silico and In Vitro Study. Mol Basel Switz. 2020;25(20).
Hariono M, Rollando R, Yoga I, Harjono A, Suryodanindro A, Yanuar M, Gonzaga T, Parabang Z, Hariyono P, Febriansah R, Hermawansyah A, Setyani W, Wahab H. Bioguided Fractionation of Local Plants against Matrix Metalloproteinase9 and Its Cytotoxicity against Breast Cancer Cell Models: In Silico and In Vitro Study (Part II). Mol Basel Switz. 2021;26(5):1464.
Rollando R, Warsito W, Masruri M, Widodo W. Pterygota alata (Roxb.) R.Br. Bark Fraction Induced Intrinsic Apoptotic Pathway in 4T1 Cells by Decreasing Bcl-2 and Inducing Bax Expression. Pak J Biol Sci PJBS. 2021;24(2):172–81.
Iskandar D, Widodo N, Warsito W, Masruri M, Rollando R, Warsidah W, Antang, YPP. Proposed Functional Activity of Bioactive Compounds from Spatholobus littoralis Hassk in LC-MS-MS and Silico Studies. Mater Sci Forum. 2022;1061:181–6.
Rollando R, Warsito W, Masruri M, Widodo N. Potential matrix metalloproteinase-9 inhibitor of aurone compound isolated from Sterculia quadrifida leaves: In-vitro and insilico studies. Res J Pharm Technol. 2022;15(11):5250–4.
Astuti P, Rollando R, Wahyuono S, Nurrochmad A. Antimicrobial activities of isoprene compounds produced by an endophytic fungus isolated from the leaves of Coleus amboinicus Lour. J Pharm Pharmacogn Res. 2020;8(4):280– 9.
Pires DEV, Blundell TL, Ascher DB. pkCSM: Predicting Small-Molecule Pharmacokinetic and Toxicity Properties Using Graph-Based Signatures. J Med Chem. 2015;58(9):4066–72.
Chen X, Li H, Tian L, Li Q, Luo J, Zhang Y. Analysis of the Physicochemical Properties of Acaricides Based on Lipinski’s Rule of Five. J Comput Biol J Comput Mol Cell Biol. 2020;27(9):1397–406.
Rollando R, Warsito W, Masruri M, Widodo W. Sterculia foetida Leaf Fraction Against Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Protein and 4T1 Breast Cancer Cells: In-Vitro and In-Silico Studies. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2021;5(1):113–21.
Chagas CM, Moss S, Alisaraie L. Drug metabolites and their effects on the development of adverse reactions: Revisiting Lipinski’s Rule of Five. Int J Pharm. 2018;549(1–2):133–49.
Protti ÍF, Rodrigues DR, Fonseca SK, Alves RJ, de Oliveira RB, Maltarollo VG. Do Drug-likeness Rules Apply to Oral Prodrugs? ChemMedChem. 2021;16(9):1446–56.
Carmichael N, Day PJR. Cell Surface Transporters and Novel Drug Developments. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:852938.
Rani I, Goyal A, Sharma M. Computational Design ofPhosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Inhibitors. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2022;20(7):317–37.
Kashyap D, Jakhmola S, Tiwari D, Kumar R, Moorthy NSHN, Elangovan M, Brás, NF, Jha HC. Plant derived active compounds as potential anti SARS-CoV-2 agents: an insilico study. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40(21):10629–50.
Rollando R, Warsito W, Masruri M, Nashi W. Antibacterial, Antioxidant, and Cytotoxic Flavonoid Compound from Sterculia quadrifida Leaves. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2021;5(11):1979–85.
de Castro Barbosa E, Alves TMA, Kohlhoff M, Jangola STG, Pires DEV, Figueiredo ACC, Alves ÉAR, Calzavara-Silva CE, Sobral M, Kroon EG, Rosa LH, Zani CL, de Oliveira JG. Searching for plant-derived antivirals against dengue virus and Zika virus. Virol J. 2022;19(1):31.
Pou Casellas C, Jansen K, Rookmaaker MB, Clevers H, Verhaar MC, Masereeuw R. Regulation of solute carriers oct2 and OAT1/3 in the kidney: a phylogenetic, ontogenetic, and cell dynamic perspective. Physiol Rev. 2022;102(2):993–1024.
Rollando R, Monica E, Aftoni MH. In vitro Cytotoxic Potential of Sterculia quadrifida Leaf Extract Against Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines:
doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v6i8.12. Trop J Nat Prod Res TJNPR. 2022;6(8):1228–32.
Hussain Z, Zhu J, Ma X. Metabolism and Hepatotoxicity of Pyrazinamide, an Antituberculosis Drug. Drug Metab Dispos Biol Fate Chem. 2021;49(8):679–82.
Hoelz LV, Calil FA, Nonato MC, Pinheiro LC, Boechat N. Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase: a drug target against malaria. Future Med Chem. 2018;10(15):1853–74.
Owoloye A, Enejoh OA, Akanbi OM, Bankole OM. Molecular docking analysis of Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase towards the design of effective inhibitors. Bioinformation. 2020;16(9):672–8.
Boschi D, Pippione AC, Sainas S, Lolli ML. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors in anti-infective drug research. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;183:111681.
Ross LS, Lafuente-Monasterio MJ, Sakata-Kato T, Mandt REK, Gamo FJ, Wirth DF, Lukens AK. Identification of Collateral Sensitivity to Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase Inhibitors in Plasmodium falciparum. ACS Infect Dis. 2018;4(4):508–15.
Pippione AC, Sainas S, Goyal P, Fritzson I, Cassiano GC, Giraudo A, Giorgis M, Tavella TA, Bagnati R, Rolando B, Caing-Carlsson R, Costa FTM, Andrade CH, Al-Karadaghi S, Boschi D, Friemann R, Lolli ML. Hydroxyazole scaffoldbased Plasmodium falciparum dihydroorotate dehydrogenase inhibitors: Synthesis, biological evaluation and X-ray structural studies. Eur J Med Chem. 2019;163:266–80.
Singh N, Chevé G, Avery MA, McCurdy CR. Targeting the methyl erythritol phosphate (MEP) pathway for novel antimalarial, antibacterial and herbicidal drug discovery: inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5-phosphate reductoisomerase (DXR) enzyme. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13(11):1161–77.
Yuniati Y, Yuliati L, Monica E, Rollando R. Discovering anticancer compound of ethyl acetate extract from RL1 code endophytic fungi culture derived by Phyllanthus niruri Linn leaves through cell cycle modulation in T47d cells. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. 2019;509:012157
Jackson ER, Dowd CS. Inhibition of 1-deoxy-D-xylulose-5- phosphate reductoisomerase (Dxr): a review of the synthesis and biological evaluation of recent inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2012;12(7):706–28.
Carretero-Paulet L, Lipska A, Pérez-Gil J, Sangari FJ, Albert VA, Rodríguez-Concepción M. Evolutionary diversification and characterization of the eubacterial gene family encoding DXR type II, an alternative isoprenoid biosynthetic enzyme. BMC Evol Biol. 2013;13:180.
Fonseca AL da, Nunes RR, Braga VML, Comar M, Alves RJ, Varotti F de P, Tarant AG. Docking, QM/MM, and molecular dynamics simulations of the hexose transporter from Plasmodium falciparum (PfHT). J Mol Graph Model. 2016;66:174–86.
Owoloye AJ, Ligali FC, Enejoh OA, Musa AZ, Aina O, Idowu ET, Oyebola KM. Molecular docking, simulation and binding free energy analysis of small molecules as PfHT1 inhibitors. PloS One. 2022;17(8):e0268269.
Jiang X, Yuan Y, Huang J, Zhang S, Luo S, Wang N, Pu D, Zhao N, Tang Q, Hirata K, Yang X, Jiao Y, Sakata-Kato T, Wu JW, Yan C, Kato N, Yin H, Yan N. Structural Basis for Blocking Sugar Uptake into the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 2020;183(1):258-268.e12.
Altharawi A, Riadi Y, Tahir Ul Qamar M. An in silico quest for next-generation antimalarial drugs by targeting Plasmodium falciparum hexose transporter protein: a multipronged approach. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2023;1–10.
Chaianantakul N, Sungkapong T, Supatip J, Kingsang P, Kamlaithong S, Suwanakitti N. Antimalarial effect of cell penetrating peptides derived from the junctional region of Plasmodium falciparum dihydrofolate reductasethymidylate synthase. Peptides. 2020;131:170372.
Vanichtanankul J, Yoomuang A, Taweechai S, Saeyang T, Pengon J, Yuvaniyama J. Structural Insight into Effective Inhibitors’ Binding to Toxoplasma gondii Dihydrofolate
Reductase Thymidylate Synthase. ACS Chem Biol. 2022;17(7):1691–702.
Seetin S, Saparpakorn P, Vanichtanankul J, Vitsupakorn D, Yuthavong Y, Kamchonwongpaisan S, Hannongbua S. Key interactions of pyrimethamine derivatives specific to wildtype and mutant P. falciparum dihydrofolate reductase based on 3D-QSAR, MD simulations and quantum chemical
calculations. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;1–16.
Melaku Y, Solomon M, Eswaramoorthy R, Beifuss U, Ondrus V, Mekonnen Y. Synthesis, antiplasmodial activity and in silico molecular docking study of pinocembrin and its analogs. BMC Chem. 2022;16(1):36.
Blomqvist K, Helmel M, Wang C, Absalon S, Labunska T, Rudlaff RM, Adapa S, Jiang R, Steen H, Dvorin JD. Influence of Plasmodium falciparum Calcium-Dependent Protein Kinase 5 (PfCDPK5) on the Late Schizont Stage Phosphoproteome. mSphere. 2020;5(1):e00921-19.
Wilde ML, Triglia T, Marapana D, Thompson JK, Kouzmitchev AA, Bullen HE, ilson PR, Cowman AF, Tonkin CJ. Protein Kinase A Is Essential for Invasion of Plasmodium falciparum into Human Erythrocytes. mBio. 2019;10(5):e01972-19.
Eck T, Laureano de Souza M, Delvillar M, Ashraf K, Yadav Bheemanaboina RR, Chakrasali R, Kreiss T, Siekierka JJ, Rotella DP, Bhanot P, Goodey NM. Characterization of Competitive Inhibitors of Plasmodium falciparum cGMPDependent Protein Kinase. Chembiochem Eur J Chem Biol.
;23(7):e202100704.
Ong HW, Truong A, Kwarcinski F, de Silva C, Avalani K, Havener TM, Chirgwin M, Galal KA, Willis C, Krämer A, Liu S, Knapp S, Derbyshire ER, Zutshi R, Drewry DH. Discovery of potent Plasmodium falciparum protein kinase 6 (PfPK6) inhibitors with a type II inhibitor pharmacophore. Eur J Med Chem. 2023;249:115043.
Hodder AN, Christensen J, Scally S, Triglia T, Ngo A, Birkinshaw RW, Bailey B, Favuzza P, Dietrich MH, Tham WH, Czabotar PE, Lowes K, Guo Z, Murgolo N, Lera Ruiz M de, McCauley JA, Sleebs BE, Olsen D, Cowman AF. Basis for drug selectivity of plasmepsin IX and X inhibition in Plasmodium falciparum and vivax. Struct Lond Engl 1993. 2022;30(7):947-961.e6.
Polino AJ, Miller JJ, Bhakat S, Mukherjee S, Bobba S, Bowman GR, oldberg DE. The nepenthesin insert in the Plasmodium falciparum aspartic protease plasmepsin V is necessary for enzyme function. J Biol Chem. 2022;298(9):102355.
Miller Iii WA, Teye J, Achieng AO, Mogire RM, Akala H, Ong’echa JM, Rathi B, Durvasula R, Kempaiah P, Kwofie SK. Antimalarials: Review of Plasmepsins as Drug Targets and HIV Protease Inhibitors Interactions. Curr Top Med Chem. 2019;18(23):2022–8.
Duanguppama J, Mathema VB, Tripura R, Day NPJ, Maxay M, Nguon C, von Seidlein L, Dhorda M, Peto TJ, Nosten F, White NJ, Dondorp AM, Imwong M. Polymorphisms in Pvkelch12 and gene amplification of Pvplasmepsin4 in Plasmodium vivax from Thailand, Lao PDR and Cambodia. Malar J. 2019;18(1):114.
Win KN, Manopwisedjaroen K, Phumchuea K, Suansomjit C, Chotivanich K, Lawpoolsri S, Cui L, Sattabongkot J, Nguitragool W. Molecular markers of dihydroartemisininpiperaquine resistance in northwestern Thailand. Malar J. 2022;21(1):352.
Santana LF, Inada AC, Espirito Santo BLS do, Filiú WFO, Pott A, Alves FM, Guimarães R. de CA, Freitas K de C, Hiane PA. Nutraceutical Potential of Carica papaya in Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients. 2019;11(7):1608.
Fallatah O, Georges E. Apigenin-induced ABCC1-mediated efflux of glutathione from mature erythrocytes inhibits the proliferation of Plasmodium falciparum. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2017;50(5):673–7.
Heller LE, Goggins E, Roepe PD. DihydroartemisininFerriprotoporphyrin IX Adduct Abundance in Plasmodium falciparum Malarial Parasites and the Relationship to Emerging Artemisinin Resistance. Biochemistry. 2018;57(51):6935–45.
Siddiqui FA, Boonhok R, Cabrera M, Mbenda HGN, Wang M, Min H, Liang X, Qin J, Zhu X, Miao J, Cao Y, Cui L. Role of Plasmodium falciparum Kelch 13 Protein Mutations in P. falciparum Populations from Northeastern Myanmar in Mediating Artemisinin Resistance. mBio. 2020;11(1):e01134-19.
Heller LE, Roepe PD. Quantification of Free Ferriprotoporphyrin IX Heme and Hemozoin for Artemisinin Sensitive versus Delayed Clearance Phenotype Plasmodiumfalciparum Malarial Parasites. Biochemistry. 2018;57(51):6927–34.
Collier TA, Piggot TJ, Allison JR. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Proteins. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2020;2073:311–27.
Hildebrand PW, Rose AS, Tiemann JKS. Bringing Molecular Dynamics Simulation Data into View. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019;44(11):902–13.