Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles from two Species of Malvaceae: Synthesis, Antimalarial, Antitrypanosomal, Antimicrobial Properties and their Potential towards HeLa Cell Line http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v7i3.26
Main Article Content
Abstract
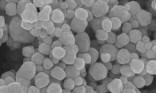
Both Gossypium barbadense (GB) and Gossypium hirsitum (GH) are members of the Malvaceae family and the cotton genus. In order to reduce silver nitrate, aqueous extracts of both plants were used to synthesize biogenic silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) (AgNO3). The techniques employed to describe them included X-ray diffraction, ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and the fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) spectrophotometer. The AgNPs were found to be crystalline according to the XRD spectra, but TEM images showed that they were evenly distributed, free of aggregation, and in irregular shapes with an average size of 21 nm. Only silver, oxygen, and carbon were present in the nanoparticles, according to the SEM and EDX data. Both AgNPs have excellent antimalarial efficacy when tested in vitro with Plasmodium falciparum, with IC50 values of 1.2 and 0.96 g/mL, weak antitrypanosomal potentials, and a good track record of negligible cytotoxicity against the HeLa cell line. Both AgNPs exhibit potent antiplasmodial and antibacterial characteristics, making them intriguing candidates for use in nanomedicines and other contexts where related applications are needed. The aim of this study is to biogenically synthesize silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using the aqueous leaf extracts of GB and GH, analyze their ability to target the HeLa cell line, and determine whether they have antimalarial and
antitrypanosomal properties.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Saibu GM, Vincent NM, Omowunmi OA, Opeoluwa OO, Olawale FO, Meyer M. In-vitro Cytotoxicity, Anti-bacterial
and Anti-inflammatory Activities of Ecklonia radiata and Jania verrucosa from Eastern Cape, South Africa:
http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v7i1.6. Trop. J. Nat. Prod. Res, 7(1), 2122–2127.
Assi GA, Al-Bashaereh A, Alsarayreh A, Al Qaisi Y, AlMajali I, Khleifat K, Alqaraleh M, Qaralleh H, Al-Farrayeh, I. Evaluation of Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Antiinflammatory Properties of Methanol Extract of Varthemia iphionoides:http://www.doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v7i1.4. Trop . J. Nat. Prod. Res. 2023; 7(1):2107–2114.
Sivasankar M, Kumar BP. Role of nanoparticles in drug delivery system. Int J. Res. Pharm. Biomed Sci. 2010;
(2):41-66.
Zhang L, Gu FX, Chan JM, Wang AZ, Langer RS, Farokhzad OC. Nanoparticles in medicine: therapeutic applications and developments. Clin. Pharm. therap. 2008; 83(5):761-9.
AbdelHamid AA, Al-Ghobashy MA, Fawzy M, Mohamed MB, Abdel-Mottaleb MM. Phytosynthesis of Au, Ag, and
Au–Ag bimetallic nanoparticles using aqueous extract of sago pondweed (Potamogetonpectinatus L.). ACS Sustain.
Chem Eng. 2013; 8;1(12):1520-9.
Malarkodi C, Rajeshkumar S, Vanaja M, Paulkumar K, Gnanajobitha G, Annadurai G. Eco-friendly synthesis and
characterization of gold nanoparticles using Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Nanostructure Chem. 2013; 1; 3(1):30.
Oluwafemi OS, Ncapayi V, Olubomehin O, Osibote OA, Songca SP. A facile non-organometallic synthesis of hexadecylamine-capped ZnSe nanoparticles. Mater Sci Semicond Process. 2014; 1:27:427-32.
Tran QH, Le AT. Silver nanoparticles: synthesis, properties, toxicology, applications and perspectives. Advances in
Natural Sciences: Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2013; 14; 4(3):033001.
Xiong J, Wang Y, Xue Q, Wu X. Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using L-ascorbic
acid. Green Chem. 2011; 13(4):900-4.
Kumar V, Yadav SK. Plant‐mediated synthesis of silver and gold nanoparticles and their applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol: International Research in Process, Environmental & Clean Technology. 2009; 84(2):151-7.
Kulkarni N, Muddapur U. Biosynthesis of metal nanoparticles: a review. J. Nanotechnol. 2014.
Tagad CK, Dugasani SR, Aiyer R, Park S, Kulkarni A, Sabharwal S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles and
their application for the development of optical fiber based hydrogen peroxide sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013; 5;
:144-9.
Saxena A, Tripathi RM, Zafar F, Singh P. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using aqueous solution of Ficus
benghalensis leaf extract and characterization of their antibacterial activity. Mater. lett. 2012; 15;67(1):91-4.
Ravichandran V, Vasanthi S, Shalini S, Shah SA, Harish R. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Atrocarpus altilis leaf extract and the study of their antimicrobial and antioxidant activity. Mater. lett. 2016; 1;180:264-7.
Dhand V, Soumya L, Bharadwaj S, Chakra S, Bhatt D, Sreedhar B. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using
Coffea arabica seed extract and its antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng: C. 2016; 1; 58:36-43.
Kumar VA, Uchida T, Mizuki T, Nakajima Y, Katsube Y, Hanajiri T, Maekawa T. Synthesis of nanoparticles composed of silver and silver chloride for a plasmonic photocatalyst using an extract from a weed Solidago altissima (goldenrod). Advances in Natural Sciences: Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2016; 8; 7(1):015002.
Park Y, Hong YN, Weyers A, Kim YS, Linhardt RJ.Polysaccharides and phytochemicals: a natural reservoir for
the green synthesis of gold and silver nanoparticles. IET nanobiotechnol. 2011; 5(3): pp69-78.
Malakotian M, Hosseini M, Bahrami H. Survey of the parasires of vegetable in Kerman province. Hormozgan Med.
J University. 2009; 13(1):55-62.
Greenwood BM, Fidock DA, Kyle DE, Kappe SH, Alonso PL, Collins FH, Duffy PE. Malaria: progress, perils, and
prospects for eradication. J. clin investig. 2008; 1; 118(4):1266-76.
Navarrete-Vazquez G, Chávez-Silva F, Argotte-Ramos R, del Carmen Rodríguez-Gutiérrez M, Chan-Bacab MJ,
Cedillo-Rivera R, Moo-Puc R, Hernández-Nuñez E. Synthesis of benzologues of Nitazoxanide and Tizoxanide: a comparative study of their in vitro broad-spectrum antiprotozoal activity. Bioorganic Med. Chem lett. 2011; 15;
(10):3168-71.
Wendel JF, Brubaker C, Alvarez I, Cronn R, Stewart JM. Evolution and natural history of the cotton genus. Genetics
and genomics of cotton 2009 (pp. 3-22). Springer, New York, NY.
Coutinho EM. Gossypol: a contraceptive for men. Contraception. 2002; 1; 65(4):259-63.
Mansour MH, Zohdy NM, El‐Gengaihi SE, Amr AE. The relationship between tannins concentration in some cotton
varieties and susceptibility to piercing sucking insects. J. Appl Entomol. 1997; 12;121(1‐5):321-5.
Mans D, Toelsie J, Jagernath Z, Ramjiawan K, van Brussel A, Jhanjan N, Orie S, Muringen M, Elliot U, Jurgens S,
Macnack R. Assessment of eight popularly used plantderived preparations for their spasmolytic potential using the
isolated guinea pig ileum. Pharm. Biol. 2004; 42(6):422-9.
Larayetan R, Ojemaye MO, Okoh OO, Okoh AI. Silver nanoparticles mediated by Callistemon citrinus extracts and
their antimalaria, antitrypanosoma and antibacterial efficacy. J. Mol. Liq. 2019; 1; 273:615-25.
Makler MT, Ries JM, Williams JA, Bancroft JE, Piper RC, Gibbins BL, Hinrichs DJ. Parasite lactate dehydrogenase as
an assay for Plasmodium falciparum drug sensitivity. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg. 1993; 48(6):739-41.
Collins CH, Lyne PM, Grange JM. JO Fal inham III. Collins and Lyne’s Microbiol Methods, 8th edition, Arnold, London.
Larayetan RA, Okoh OO, Sadimenko A, Okoh AI. Terpene constituents of the aerial parts, phenolic content, antibacterial potential, free radical scavenging and antioxidant activity of Callistemon citrinus (Curtis) Skeels (Myrtaceae) from Eastern Cape Province of South Africa. BMC Complement Altern. med. 2017; 17(1):292.
Keusch GT, Jacewicz M, Hirschman SZ. Quantitative microassay in cell culture for enterotoxin of Shigella dysenteriae 1. J. Infect. Dis. 1972; 125(5):539-41.
Ajayi A, Larayetan R, Yahaya A, Falola OO, Ude NA, Adamu H, Oguche SM, Abraham K, Egbagba AO, Egwumah
C, Ojochegbe SO. Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles with bitter leaf (Vernonia amygdalina) aqueous extract and
its effects on testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in Wistar rat. Chemistry Africa. 2021;
(4):791-807.
KS US, Govindaraju K, Kumar G, Prabhu D, Arulvasu C, Karthick V, Changmai N. Anti-proliferative effect of biogenic gold nanoparticles against breast cancer cell linesmj (MDA-MB-231 & MCF-7). Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016; 371:415- 24.
McCoy ME, Golden HE, Doll TA, Yang Y, Kaba SA, Burkhard P, Lanar DE. Mechanisms of protective immune
responses induced by the Plasmodium falciparum circumsporozoite protein-based, self-assembling protein nanoparticle vaccine. Malaria journal. 2013; 12(1):136.
Rotimi L, Ojemaye MO, Okoh OO, Sadimenko A, Okoh AI. Synthesis, characterization, antimalarial, antitrypanocidal
and antimicrobial properties of gold nanoparticle. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2019; 2; 12(1):61-8.
Bero J, Beaufay C, Hannaert V, Hérent MF, Michels PA, Quetin-Leclercq J. Antitrypanosomal compounds from the
essential oil and extracts of Keetia leucantha leaves with inhibitor activity on Trypanosoma brucei glyceraldehyde-3-
phosphate dehydrogenase. Phytomedicine. 2013; 20(3- 4):270-4.
Ajitha B, Reddy YA, Reddy PS. Biogenic nano-scale silver particles by Tephrosia purpurea leaf extract and their inborn
antimicrobial activity. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014; 121:164-72.
Hajipour MJ, Fromm KM, Ashkarran AA, de Aberasturi DJ,de Larramendi IR, Rojo T, Serpooshan V, Parak WJ,
Mahmoudi M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012; 30(10):499-511.
Nel AE, Madler L, Velegol D, Xia T, Hoek EMV,Somasundaran P. Nat. Mater. 2009; 8 543.
Sondi I, Salopek-Sondi B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for
Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface sci. 2004; 275(1):177-82.
Marambio-Jones C, Hoek EM. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2010; 12(5):1531-51.