Safety Evaluation of Sub-acute and Acute Oral Treatment with Aqueous Extract and Methanol Fraction of Aloe barbadensis (Aloe vera) Leaves in Wistar Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
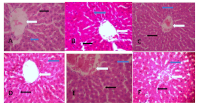
Ethnobotanicals continue to gain global relevance due to their therapeutic potential and their role as precursors in pharmaceutical development. Aloe barbadensis is one of the most common traditional herbs in Nigeria, particularly for its purported antimalarial properties. The increasing use of traditional remedies in malaria-endemic regions like Nigeria makes it imperative to conduct regular safety assessments of medicinal plants. This study investigates the safety of A. barbadensis by assessing its acute and subacute toxicity. The plant was collected from Oke-Aluko farm in Ilorin, Nigeria, and authenticated by a botanical expert. Both aqueous extract and a methanol fraction of A. barbadensis leaves were prepared for the study. Wistar rats were administered single oral doses of 2000, 5000, and 6000 mg/kg, followed by a 14-day observation period to assess acute toxicity and potential delayed effects. For the subacute toxicity testing, daily doses of 250, 500, and 750 mg/kg were administered over 28 days. The liver functions (AST, ALT, ALP, GGT), kidney functions (urea, creatinine, sodium, potassium), haematological parameters, and histological analyses of the organs were evaluated. Results showed no significant adverse effects on biochemical or haematological parameters (p > 0.05) at all doses in both study phases. However, continuous treatment with the methanol fraction at 750 mg/kg led to histopathological changes in the liver and kidney after 28 days, indicating potential organ toxicity at higher doses. This study advocates for the extract dose regulation and future long-term chronic toxicity studies on the plant.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1. Pranto TI, Ullah MR, Rahman MM, Shohan F, Baroi JA, Bhowmik P, Rupak MA, Chowdhury T, Tashin R. An Assessment of Hepatoprotective Activity of Aloe barbadensis on Rat Model with Safety Profile Analysis. Asian J. Res. Rep. Hepatol. 2024;6(1):1-7.
2. Mensah ML, Komlaga G, Forkuo AD, Firempong C, Anning AK, Dickson RA. Toxicity and Safety Implications of Herbal Medicines. Herbal medicine. 2019:63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.72437
3. Tong X, Li M, Li D, Lao C, Chen J, Xu W, Du J, Zhang M, Yang X, Li J. Aloe vera gel extract: Safety evaluation for acute and chronic oral administration in Sprague-Dawley rats and anticancer activity in breast and lung cancer cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021; 280:114434. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114434
4. Chaachouay N, Zidane L. Plant-derived natural products: a source for drug discovery and development. Drugs Drug Candidates. 2024;3(1):184-207. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ddc3010011
5. Sánchez M, González-Burgos E, Iglesias I, Gómez-Serranillos MP. Pharmacological update properties of aloe vera and its major active constituents. Molecules. 2020;25(6):1–38. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061324
6. Mishra I, Soni H, Soni J, Sing RK. A study on the ethnopharmacological potential of Aloe vera l. Int J Pharmacogn. 2024;11(11):577–83.
7. Kumar S, Yadav M, Yadav A, Rohilla P, Yadav JP. Antiplasmodial potential and quantification of aloin and aloe-emodin in Aloe vera collected from different climatic regions of India. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017;17:369. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-017-1883-0
8. Asiimwe, S., Namutebi, A., Borg-Karlson, A. K., Mugisha, M. K., Kakudidi, E. K., Hannington OO. Documentation and consensus of indigenous knowledge on medicinal plants used by the local communities of western Uganda. J Nat Prod Plant Resour. 2014;4(1):34–42.
9. Bendjedid S, Bazine I, Tadjine A, Djelloul R, Boukhari A, Bensouici C. Analysis of Phytochemical Constituents by using LC-MS, Antifungal and Allelopathic Activities of Leaves Extracts of Aloe vera. Jordan J Biol Sci. 2022;15(1):21–28. DOI: https://doi.org/10.54319/jjbs/150104
10. Adeyemi OF, Okungbowa GE, Ogbeide OU. Aloe vera prevents radiation-induced dermatitis among the black population. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2018;2(9):433–437. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v2i9.5
11. Amro BI, Abu Hajleh MN, Afifi F. Evidence-based potential of some edible, medicinal and aromatic plants as safe cosmetics and cosmeceuticals. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2021;5(1):16–18. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v5i1.3
12. Abeer M. El Sayeda, Shahira M. Ezzata, Moataz M. El Naggarb SSEH. In vivo diabetic wound healing effect and HPLC – DAD – ESI – MS / MS profiling of the methanol extracts of eight Aloe species. Brazillian J Pharmacogn. 2016;26:352–362. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2016.01.009
13. Dharajiya D, Pagi N, Jasani H, Patel P. Antimicrobial activity and phytochemical screening of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller). Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci. 2017; 6(3):2152-2162. DOI: https://doi.org/10.20546/ijcmas.2017.603.246
14. Bello R, Muhammad I, Ali H. Quantitative and qualitative phytochemicals and proximate analysis of aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis miller). Int J Adv Acad Res. 2020;6(1):95-109.
15. Raad B. Phytochemical screening and biological activities of Aloe vera (L.) Burm. F. Pure Appl Biol. 2021;10(1):360–367. DOI: https://doi.org/10.19045/bspab.2021.100039
16. López A, De Tangil MS, Vega-Orellana O, Ramírez AS, Rico M. Phenolic constituents, antioxidant and preliminary antimycoplasmic activities of leaf skin and flowers of Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f.(syn. A. barbadensis Mill.) from the Canary Islands (Spain). Molecules. 2013;18(5):4942-4954. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules18054942
17. Shabnam K, Ram TC, Ashaq M. Aloe Vera : A Systematic Review from the Perspectives of the Food Industries and Medicinal Applications. African J Biol Sci. 2024;6(6):8198–8215.
18. Cordiano R, Caserta S, Minciullo PL, Allegra A, Gangemi S. Anthraquinones and Aloe Vera Extracts as Potential Modulators of Inflammaging Mechanisms: A Translational Approach from Autoimmune to Onco-Hematological Diseases. Molecules. 2025;30(6):1–29. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30061251
19. Mensah EO, Adadi P, Asase RV, Kelvin O, Mozhdehi FJ, Amoah I, Agyei D. Aloe vera and its byproducts as sources of valuable bioactive compounds: Extraction, biological activities, and applications in various food industries.PharmaNutrition. 2025;31:100436. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2025.100436 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phanu.2025.100436
20. OECD 2008. Repeated Dose 28-Day Oral Toxicity Study in Rodents (OECD TG 407). 2008; 477–90.
21. Adebayo G, Ayanda OI, Rottmann M, Ajibaye OS, Oduselu G, Mulindwa J, Ajani OO, Aina O, Mäser P, Adebiyi E. The Importance of Murine Models in Determining In Vivo Pharmacokinetics, Safety, and Efficacy in Antimalarial Drug Discovery. Pharmaceuticals. 2025;18(3):424. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ph18030424
22. Ibrahim AM, Sadah H Al, Ahmad R, Ahmad N, Naqvi AA. Clinical uses and toxicity of aloe vera: An evidence-based comprehensive retrospective review (2007-2017). Pharmacogn J. 2019;11(2):424–428. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5530/pj.2019.11.66
23. Guo X, Mei N. Aloe vera: A review of toxicity and adverse clinical effects. J Environ Sci Heal - Part C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 2016;34(2):77–96. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2016.1166826 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10590501.2016.1166826
24. Arsene MM, Viktorovna PI, Sergei GV, Hajjar F, Vyacheslavovna YN, Vladimirovna ZA, Aleksandrovna VE, Nikolayevich SA, Sachivkina N. Phytochemical analysis, antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of Aloe vera aqueous extract against selected resistant gram-negative bacteria involved in urinary tract infections. Fermentation. 2022;8(11):626. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation8110626
25. Tiwari S, Sigdel S, Bhattarai S, Rokaya RK, Pandey J. Phytochemical Screening, Antibacterial ‑ Guided Fractionation, and Thin-Layer Chromatographic Pattern of the Extract Obtained from Diploknema butyracea. Pharmacognosy Res. 2021;12(2021):437–443. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/pr.pr_27_20
26. Mohr BJ, Fakoya FA, Hau J, Souilem O, Anestidou L. The governance of animal care and use for scientific purposes in Africa and the Middle East. ILAR J. 2016;57(3):333–346. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar/ilw035
27. Moronkeji A, Akinbo FO. Genotoxic Response and Histological Alterations in Rat Lungs Exposed to Gasoline Generator Exhaust. Sultan Qaboos Univ J Sci [SQUJS]. 2024;29(1):15–27. Available from: https://journals.squ.edu.om/index.php/squjs/article/view/5780 DOI: https://doi.org/10.53539/squjs.vol29isspp15-27
28. Adeniyi TD, Moronkeji, A,Ekundina VO. Histological evaluation of the liver, kidney, and testes of adult male Wistar rats exposed to heavy metals-contaminated waterways. Med Lab J. 2023;17(5):4–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.61186/mlj.17.5.4
29. Abubakar AA, Ismaila NO, Musa MA, Fadairo JK. Combined Extracts of Bryophyllum pinnatum and Aloe barbadensis Induce Hepato-renal Dysfunctions and Elevated Hematological Indices in Wistar Rats. European J Med Plants. 2014;4(8):990–997. DOI: https://doi.org/10.9734/EJMP/2014/9024
30. Moronkeji A, Adeniyi T, Olubunmi E, Kayode I, Ajala OJ, Moronkeji AI, Idowu D. Modulatory effects of Aframomum melegueta and Rauvolfia vomitoria in cadmium-induced renal toxicity in adult rats. J Cell Biotechnol. 2025,11(1):3-13. doi:10.1177/23523689251329719 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/23523689251329719
31. Moronkeji A, Eze IG, Bejide RA, Anwara OA, Igunbor MC. Evaluation of herbal cocktail used in the treatment of malaria on liver tissue of adult Wistar rats. J Med Plants Res. 2018;12(28):508–21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR2018.6661
32. Kinanthi AD, Izza LN, Muhede R, Fitri LE, Handono K, Yudharto HS, Riawan W, Khotimah H. Ethanol Extract from Yellow Pumpkin Modulate Hormonal Levels and Ovarian Follicle Dynamics in Hypoestrogenic Wistar Rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2025;9(3):1001–1010. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i3.15
33. Ekor M. The growing use of herbal medicines: Issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front Neurol. 2014;4:1–10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2013.00177
34. Adeniyi TD, Akinpelu M, Akinlami OO, Alaga FO, Adenika MM. Evaluation of the combined extract of Rauwolfia vomitoria and Aframomum melegueta on the kidney and liver of adult male Wistar rats. Sokoto J Med Lab Sci. 2024;9(2):203–212. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4314/sokjmls.v9i2.24
35. Abderrahmane F, Addou S, Labadie I, Kheroua O. Acute toxicity of the aqueous extract of Aloe barbadensis miller gel. Bangladesh J Sci Ind Res. 2023;58(1):19–34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3329/bjsir.v58i1.65110
36. Asim Kumar Ghosh, Manasi Banerjee, Tapan Kumar Mandal, Akhilesh Mishra MKB. A Study on Analgesic Efficacy and Adverse Effects of Aloe. Pharmacol 1. 2011;1108:1098 –1108.
37. Sehgal I, Winters WD, Scott M, David A, Gillis G, Stoufflet T, Nair A, Kousoulas K. Toxicologic assessment of a commercial decolorized whole leaf aloe vera juice, lily of the desert filtered whole leaf juice with aloesorb. J Toxicol. 2013;2013(1):802453. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/802453
38. Yimam M, Brownell L, Jia Q. In vivo safety evaluation of UP780, a standardized composition of aloe chromone aloesin formulated with an Aloe vera inner leaf fillet. RegulToxicolPharmacol. 2014;69(3):390–7. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.05.001 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.05.001
39. Olaniyan JM, Muhammad HL, Makun HA, Busari MB, Abdullah AS. Acute and sub-acute toxicity studies of aqueous and methanol extracts of Nelsonia campestris in rats. J Acute Dis. 2016;5(1):62–70. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2015.08.006 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joad.2015.08.006
40. Nalimu F, Oloro J, Peter EL, Ogwang PE. Acute and sub-acute oral toxicity of aqueous whole leaf and green rind extract of Aloe vera in Wistar Rats. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2022;22(1):1-14. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-021-03470-4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-021-03470-4
41. Darlington Akukwu, Ugochukwu Aguwa, Catherine Akukwu, Ambrose Agulanna, Obatavwe Ukoba IO. Effects of Aloe vera Gel on the Homeopoietic , Biochemical and Histological Parameters and Bone Marrow of Wistar Rats. South Asian Res J Nat Prod. 2023;6(3):185–95.
42. Nalimu F, Oloro J, Kahwa I, Ogwang PE. Review on the phytochemistry and toxicological profiles of Aloe vera and Aloe ferox. Futur J Pharm Sci. 2021;7:145. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s43094-021-00296-2
43. Devaraj S, Yimam M, Brownell LA, Jialal I, Singh S, Jia Q. Effects of aloe vera supplementation in subjects with prediabetes/metabolic syndrome. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2013;11(1):35–40. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1089/met.2012.0066
44. Kwack SJ, Do SG, Kim YW, Kim YJ, Gwak HM, Park HJ, Roh T, Shin MK, Lim SK, Kim HS, Lee BM. The no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) of baby aloe powder (BAP) for nutraceutical application based upon toxicological evaluation. J Toxicol Environ Heal, Part A. 2014;77(22-24):1319-1331. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2014.951590
45. Rajin M, Mawarti H, Asumta MZ. Toxicity of Aloe vera leaf Extract for multidrug-resistant (MDR) of Tuberculosis. J Appl Environ Biol Sci. 2017;7(11):153–156.
46. Koroye OC, Siminialayi IM, Etebu EN. Effects of oral administration of Aloe vera plus on the heart and kidney: a subacute toxicity study in rat models. Nig Health J 2010;10(1-2):17-21.