Metabolomics-Guided Discovery of Anticancer Metabolites from Marine Sponge-Associated Bacillus safensis: In Vitro and In Silico Evaluation
Main Article Content
Abstract
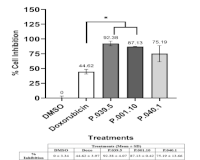
Marine-derived bacteria are valuable sources of novel anticancer agents, particularly those associated with sponges in tropical ecosystems. This study aimed to investigate the cytotoxic and metabolomic profile of Bacillus safensis P.039.5, isolated from marine sponge Petrosia nigricans collected near Pari Island, Indonesia. Cytotoxic screening against MCF-7 breast cancer cells revealed significant inhibition, with an IC50 value of 186.63 μg/mL and a high selectivity index compared to doxorubicin. Metabolite profiling using Liquid Chromatography-High Resolution Mass Spectrometry (LC-HRMS/MS) identified 28 putative compounds, dominated by peptides and alkaloids. Among these, militarinone A, maculosin, and verpacamide A showed the strongest predicted binding affinities in molecular docking studies against five breast cancer-related targets: ER-α, HER2, EGFR, CDK2, and topoisomerase IIα. Militarinone A exhibited the highest binding affinity (-11.11 kcal/mol), exceeding native ligands and reference drugs. To our knowledge, this is the first report of militarinone A detection in B. safensis P.039.5, demonstrating the utility of a metabolomics-guided approach to prioritize bioactive compounds from underexplored marine bacteria. These findings highlight the pharmacological potential of B. safensis as a sustainable source of multi-target anticancer leads.
Downloads
Article Details
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
1. Moslemi M, , Moradi Y, Dehghanbanadaki H, Afkhami H, Khaledi M, Sedighimehr N, Fathi J, Sohrabi E. The Association Between ATM Variants and Risk of Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Cancer. 2021; 21(1). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-020-07749-6
2. Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A. Global Cancer Statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024; 74(3):229–263. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21834
3. Hanstein B, Djahansouzi S, Dall P, Beckmann MW, Bender HG. Insights into The Molecular Biology of The Estrogen Receptor Define Novel Therapeutic Targets for Breast Cancer. Eur J Endocrinol. 2004; 150(3):243–255. Doi: 10.1530/eje.0.1500243 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1530/eje.0.1500243
4. Hayashi SI, Eguchi H, Tanimoto K, Yoshida T, Omoto Y, Inoue A, Yoshida N, Yamaguchi Y. The expression and function of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in human breast cancer and its clinical application. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003; 10(2):193–202. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1677/erc.0.0100193
5. Suganya J, Radha M, Naorem DL, Nishandhini M. In Silico Docking Studies of Selected Flavonoids - Natural Healing Agents Against Breast Cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014; 15(19):8155–8159. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.19.8155
6. Park M, Kim D, Ko S, Kim A, Mo K, Yoon H. Breast Cancer Metastasis: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(12):6806. Doi: 10.3390/ijms23126806. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23126806
7. Hong R, Xu B. Breast Cancer: An Up-to-date Review and Future Perspectives. Cancer Commun. 2022; 42(10): 913–936. Doi: 10.1002/cac2.12358 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/cac2.12358
8. Moslemi M, Sohrabi E, Afkhami H, Khaledi M, Azadi N, Zekri A, Razmara E. Expression Analysis of EEPD1 and MUS81 Genes in Breast Cancer. Biomed J Sci Tech Res. 2020; 29(4): 22556-22564. Doi: 10.26717/BJSTR.2020.29.004824 DOI: https://doi.org/10.26717/BJSTR.2020.29.004821
9. Palaniappan M. Palaniappan M. Current Therapeutic Opportunities for Estrogen Receptor Mutant Breast Cancer. Biomed. 2024; 12(12):2700. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122700
10. Ferro A, Campora M, Caldara A, De Lisi D, Lorenzi M, Monteverdi S, Mihai R, Bisio A, Dipasquale M, Caffo O, Ciribilli Y. Novel Treatment Strategies for Hormone Receptor (HR)-Positive, HER2-Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. J Clin Med. 2024; 13(12):3611. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123611
11. Waks AG, Winer EP. Breast Cancer Treatment: A Review. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2019; 321(3):288-300. Doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.19323 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.19323
12. Al-Zharani M, Nasr FA, Abutaha N, Alqahtani AS, Noman OM, Mubarak M, Wadaan M. Apoptotic Induction and Anti-migratory Effects of Rhazya stricta Fruit Extracts on A Human Breast Cancer Cell Line. Molecules. 2019; 24(21):3968. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24213968
13. Utami YP, Yulianty R, Djabir YY, Alam G. Anticancer Activity of Leaf Extracts and Fractions of Etlingera elatior (Jack) R.M.Sm. from North Luwu, Indonesia, using the MTT Assay Protocol. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2025; 9(2):756–764. DOI: https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i2.44
14. Al-Mahayri ZN, Patrinos GP, Ali BR. Toxicity and Pharmacogenomic Biomarkers in Breast Cancer Chemotherapy. Front Pharmacol. 2020; 11:445. Doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00445 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00445
15. Valiyaveettil D, Joseph D, Malik M. Cardiotoxicity in breast cancer treatment: Causes and mitigation. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 2023; 37:100760. Doi: 10.1016/j.ctarc.2023.100760. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctarc.2023.100760
16. Scripture CD, Figg WD, Sparreboom A. Peripheral Neuropathy Induced by Paclitaxel: Recent Insights and Future Perspectives. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2006; 4(2):165-172. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2174/157015906776359568
17. Alves C, Diederich M. Marine Natural Products as Anticancer Agents. Mar Drugs. 2021; 19(8):447. Doi: 10.3390/md19080447 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080447
18. Francesch AM, Glaser KB, Jaspars M, Jiménez C, Luesch H, Mayer AM, Newman D, Pierce ML, Taglialatela-Scafati O. Pharmaceuticals from Marine Sources: Past, Present and Future. Pharm J. 2024; 313(7987):1-37.
19. Carroll AR, Copp BR, Davis RA, Keyzers RA, Prinsep MR. Marine Natural Products. Nat Prod Rep. 2022; 39(6):1122–1171. Doi: 10.1039/D1NP00076D DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1NP00076D
20. Li P, Lu H, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Liu L, Wang M, Liu L. The Natural Products Discovered in Marine Sponge-associated Microorganisms: Structures, Activities, and Mining Strategy. Front Mar Sci. 2023; 10:1191858. Doi: 10.3389/fmars.2023.1191858 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2023.1191858
21. Nofiani R, Rudiyansyah, Ardiningsih P, Rizky, Zahra STA, Sukito A, Weisberg A, Chang J, Mahmud T. Genome Features and Secondary Metabolite Potential of The Marine Symbiont Streptomyces sp. RS2. Arch Microbiol. 2023; 205(6). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-023-03556-2
22. Hill M, Hill A, Lopez N, Harriott O. Sponge-specific Bacterial Symbionts in The Caribbean Sponge, Chondrilla nucula (Demospongiae, Chondrosida). Mar Biol. 2006; 148(6):1221–1230. Doi: 10.1007/s00227-005-0164-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-005-0164-5
23. Kuo J, Yang YT, Lu MC, Wong TY, Sung PJ, Huang YS. Antimicrobial Activity and Diversity of Bacteria Associated with Taiwanese Marine Sponge Theonella swinhoei. Ann Microbiol. 2019; 69(3):253–265. Doi: 10.1007/s13213-018-1414-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-018-1414-3
24. Aboul-Ela HM, Shreadah MA, Abdel-Monem NM, Yakout GA, Soest RWM van. Isolation, Cytotoxic Activity and Phylogenetic Analysis of Bacillus sp. Bacteria Associated with The Red Sea Sponge Amphimedon ochracea. Adv Biosci Biotechnol. 2012; 3(7):815–823. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4236/abb.2012.37101
25. Liu Y, Lai Q, Dong C, Sun F, Wang L, Li G, Shao Z. Phylogenetic Diversity of the Bacillus pumilus Group and the Marine Ecotype Revealed by Multilocus Sequence Analysis. PLoS One. 2013; 8(11):e80097. Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080097 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080097
26. Lateef A, Adelere IA, Gueguim-Kana EB. The Biology and Potential Biotechnological Applications of Bacillus safensis. Biologia (Bratisl). 2015; 70(4):411–419. Doi: 10.1515/biolog-2015-0062 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/biolog-2015-0062
27. Saidumohamed BE, Baburaj AP, Johny TK, Sheela UB, Sreeranganathan M, Bhat SG. A magainin-2 like bacteriocin BpSl14 with anticancer action from fish gut Bacillus safensis SDG14. Anal Biochem. 2021; 627:114261. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2021.114261
28. Padayao MHR, Padayao FRP, Patalinghug JM, Raña GS, Yee J, Geraldino PJ, Quilantang N. Antimicrobial and Quorum Sensing Inhibitory Activity of Bacillus safensis EPB9 Isolated from The Red Alga Halymenia durvillei. Access Microbiol. 2023; 5(12):000563.v4. Doi: 10.1099/acmi.0.000563.v4 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1099/acmi.0.000563.v4
29. Kim GJ, Li X, Kim SH, Yang I, Hahn D, Chin J, Nam SJ, Nam JW, Nam DH, Oh DC, Chang HW, Choi H. Seongsanamides A-D: Antiallergic Bicyclic Peptides from Bacillus safensis KCTC 12796BP. Org Lett. 2018; 20(23):7539–7543. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03293
30. Niles AL, Moravec RA, Riss TL. Update on In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assays for Drug Development. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2008; 3(6):655–669. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1517/17460441.3.6.655
31. Naz S, Gallart-Ayala H, Reinke SN, Mathon C, Blankley R, Chaleckis R, Wheelock CE. Development of a Liquid Chromatography–High Resolution Mass Spectrometry Metabolomics Method with High Specificity for Metabolite Identification Using All Ion Fragmentation Acquisition. Anal Chem. 2017; 89(15):7933–7942. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b00925
32. Wolfender JL, Nuzillard JM, van der Hooft JJJ, Renault JH, Bertrand S. Accelerating Metabolite Identification in Natural Product Research: Toward an Ideal Combination of Liquid Chromatography–High-Resolution Tandem Mass Spectrometry and NMR Profiling, in Silico Databases, and Chemometrics. Anal Chem. 2019; 91(1):704–742. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05112
33. Al Mousa AA, Abouelela ME, Mansour A, Nasr M, Ali YH, Al Ghamidi NS, Abo-Dahab Y, Mohamed H, Abo-Dahab NF, Hassane AMA. Wound Healing, Metabolite Profiling, and In Silico Studies of Aspergillus terreus. Issues Mol Biol. 2024; 46:11681–11699. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/cimb46100694
34. Wibowo JT, Rachman F, Untari F, Zedta RR, Utama RS, Handayani I, Setiawan R, Hertiani T. Exploring Marine Invertebrate-Associated Bacteria for Novel Antibiotics Discovery. Indonesian J. Pharm. 2025; 36(1):64–73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.22146/ijp.11217
35. Mosmann T. Rapid Colorimetric Assay for Cellular Growth and Survival: Application to Proliferation and Cytotoxicity Assays. J Immunol Methods. 1983; 65:55-63. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1759(83)90303-4
36. Chen YH, Yang JC, Lu MC, Weng CF, Su Y Di, Kuo J, Wu YC, Sung PJ. Bafilomycins N and O, novel cytotoxic bafilomycin analogues produced by Streptomyces sp. GIC10-1 isolated from marine sponge Theonella sp. Tetrahedron. 2017; 73(34):5170–5175. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2017.07.009
37. Febriansah R, Hertiani T, Widada J, Taher M, Damayanti E, Mustofa M. Isolation of active compounds from Streptomyces sennicomposti GMY01 and cytotoxic activity on breast cancer cells line. Heliyon. 2024; 10(2). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24195
38. Singh K, Gangrade A, Jana A, Mandal BB, Das N. Design, Synthesis, Characterization, and Antiproliferative Activity of Organoplatinum Compounds Bearing a 1,2,3-Triazole Ring. ACS Omega. 2019; 4(1):835–841. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b02849
39. Priyanto JA, Purwaningtyas WE, Ferantika D, Tohir D, Astuti RI, Wahyudi AT. Natural extracts derived from marine sponge-associated bacteria with diverse nonribosomal peptide synthetase genes have anticancer activities. J Appl Pharm Sci. 2022; 12(4):054–063. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2022.120406
40. Chalita M, Kim YO, Park S, Oh HS, Cho JH, Moon J, Baek N, Moon C, Lee K, Yang J, Nam GG, Jung Y, Na SI, Bailey MJ, Chun J. EzBioCloud: a genome-driven database and platform for microbiome identification and discovery. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2024; 74(6). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.006421
41. Wang F, Allen D, Tian S, Oler E, Gautam V, Greiner R, Metz TO, Wishart DS. CFM-ID 4.0 – A web server for accurate MS-based metabolite identification. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022; 50(W1):W165–W174. Doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac383 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkac383
42. Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem. 2004; 25(13):1605–1612. Doi: 10.1002/jcc.20084 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
43. Hernández-Santoyo A, Tenorio-Barajas AY, Victor Altuzar, Vivanco-Cid H, Mendoza-Barrera C. Protein-Protein and Protein-Ligand Docking. In: Ogawa T (Eds). Protein Engineering -Technology and Application. Croatia: IntechOpen. 2013. 63-80 p. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5772/56376
44. Zuhri UM, Yuliana ND, Fadilah F, Erlina L, Purwaningsih EH, Khatib A. Exploration of the main active metabolites from Tinospora crispa (L.) Hook. f. & Thomson stem as insulin sensitizer in L6.C11 skeletal muscle cell by integrating in vitro, metabolomics, and molecular docking. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024; 319(Pt 3):117296. Doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.117296 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2023.117296
45. Fadilah F, Arsianti A, Kusmardi K, Tedjo A. Molecular Docking Studies of Opened-Chain Analogues of Antimycin A3 As Caspases Inhibitors of Apoptosis in Colorectal Cancer. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2016; 9(3):350–352.
46. Shalini T, Manivel G, Krishna kumar G, Prathiviraj R, Rajesh Kannan V, Senthilraja P. Secondary Metabolite Profiling Using HR-LCMS, Antioxidant and Anticancer Activity of Bacillus cereus PSMS6 Methanolic Extract: In Silico and In Vitro Study. Biotechnol. Rep (Amst). 2024; 42:e00842. Doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00842 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2024.e00842
47. Field AP. Discovering Statistics using SPSS (and sex and drugs and rock ‘n’ roll). (3rd ed.). London: SAGE; 2012. 821 p.
48. Grever MR, Schepartz SA, Chabner BA. The National Cancer Institute: Cancer Drug Discovery and Development Program. Semin Oncol. 1992; 6(19):622–638.
49. Badisa RB, Darling-Reed SF, Joseph P, Cooperwood JS, Latinwo LM, Goodman CB. Selective Cytotoxic Activities of Two Novel Synthetic Drugs on Human Breast Carcinoma MCF-7 Cells. Anticancer Res. 2009; 29(8):2993
50. Lepori I, Roncetti M, Vitiello M, Barresi E, De Paolo R, Tentori PM, Baldanzi C, Santi M, Evangelista M, Signore G, Tedeschi L, Gravekamp C, Cardarelli F, Taliani S, Da Settimo F, Siegrist MS, Poliseno L. Enhancing the Anticancer Activity of Attenuated Listeria monocytogenes by Cell Wall Functionalization with “Clickable” Doxorubicin. ACS Chem Biol. 2024; 19(10):2131–2140. Doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00250 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.4c00250
51. Xuan Nhiem N, Van Quang N, Van Minh C, Thi Thuy Hang D, Le Tuan Anh H, Huu Tai B, Hai Yen P, Thi Hoai N, Cong Thung D, Van Kiem P. Biscembranoids from the Marine Sponge Petrosia nigricans. Nat Prod Commun. 2013; 8(9):1209-1212. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X1300800905
52. Abdelhameed RFA, Habib ES, Eltahawy NA, Hassanean HA, Ibrahim AK, Mohammed AF, Fayez S, Hayallah AM, Yamada K, Behery FA, Al-Sanea MM, Alzarea SI, Bringmann G, Ahmed SA, Abdelmohsen UR. New cytotoxic natural products from the red sea sponge Stylissa carteri. Mar Drugs. 2020; 18(5):241. Doi: 10.3390/md18050241. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md18050241
53. Chianese G, Fattorusso E, Taglialatela-Scafati O, Bavestrello G, Calcinai B, Dien HA, Ligresti A, Di Marzo V. Desulfohaplosamate, a new phosphate-containing steroid from Dasychalina sp., is a selective cannabinoid CB2 receptor ligand. Steroids. 2011; 76(10–11):998–1002. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.steroids.2011.03.013
54. Fujita M, Nakao Y, Matsunaga S, Seiki M, Itoh Y, van Soest RWM, Heubes M, Faulkner D, Fusetani N. Isolation and structure elucidation of two phosphorylated sterol sulfates, MT1-MMP inhibitors from a marine sponge Cribrochalina sp.: revision of the structures of haplosamates A and B. Tetrahedron. 2001; 57(18):3885–3890. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0040-4020(01)00259-9
55. Hudspith M, Rix L, Achlatis M, Bougoure J, Guagliardo P, Clode PL, Webster NS, Muyzer G, Pernice M, de Goeij JM. Subcellular view of host–microbiome nutrient exchange in sponges: insights into the ecological success of an early metazoan–microbe symbiosis. Microbiome. 2021; 9(1):44. Doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00984-w. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-020-00984-w
56. Berde CV, Berde VB, Reddy PN, Veera Bramhachari P. Bioprospection of Marine Sponge Microbiome for Bioactive Metabolites Employing Advanced Metagenomics Tools. In: Veera Bramhachari P, Berde CV, editors. MBMBPA. 2023; 15–38. Doi: 10.1007/978-981-99-6770-4_2 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-6770-4_2
57. Thite VS, Nerurkar AS, Baxi NN. Optimization of Concurrent Production of Xylanolytic and Pectinolytic Enzymes by Bacillus safensis M35 and Bacillus altitudinis J208 Using Agro-industrial Biomass through Response Surface Methodology. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):3824. Doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60760-6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60760-6
58. Iqbal S, Begum F, Qasim M. Screening, Characterization and Optimization of Bioactive Peptides with Antibacterial Activities Against Multi-Drug Resistant Pathogens, Produced by Bacillus safensis Strain MK-12.1. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2022; 28(6). DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-022-10469-z
59. Perumal L. Bioactive Compound Isolated from Marine Bacillus safensis MB8 and Their Cytotoxicity Potential. Asian J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020; 6(4):239–248. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31024/ajpp.2020.6.4.2
60. Nachimuthu S, Kathirvel P. Bioconversion of Tannery Hide into Biofertilizer using Bacillus safensis as Plant Growth Promoting Bacteria and its Efficacy for Plant Growth Study. Iran. J. Sci. 2023; 47(5):1471–1485. Doi: 10.1007/s40995-023-01542-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40995-023-01542-3
61. Roy T, Bandopadhyay A, Paul C, Majumdar S, Das N. Role of Plasmid in Pesticide Degradation and Metal Tolerance in Two Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria Bacillus cereus (NCIM 5557) and Bacillus safensis (NCIM 5558). Curr Microbiol. 2022; 79(4):106. Doi: 10.1007/s00284-022-02793-w DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02793-w
62. Zou H, Chen N, Shi M, Xian M, Song Y, Liu J. The metabolism and biotechnological application of betaine in microorganism. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016; 100(9):3865-3876. Doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7462-3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7462-3
63. Inoue N, Tsuge K, Yanagita T, Oikawa A, Nagao K. Time-Course Metabolomic Analysis: Production of Betaine Structural Analogs by Fungal Fermentation of Seaweed. Metabolites. 2024; 14(4):201. Doi: 10.3390/metabo14040201. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo14040201
64. Roberts MF, Wink M. Alkaloids: Biochemistry, Ecology, and Medicinal Applications. (1st ed.). New York: Springer; 1998. 482 p. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4757-2905-4
65. Hu S, He W, Wu G. Hydroxyproline in animal metabolism, nutrition, and cell signaling. Amino Acids. 2022; 54(4):513-528. Doi: 10.1007/s00726-021-03056-x DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-03056-x
66. Pollitt S, Hegarty MP, Pass MA. Analysis of the amino acid indospicine in biological samples by high performance liquid chromatography. Nat Toxins. 1999; 7(6):233–240 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/1522-7189(199911/12)7:6<233::AID-NT59>3.0.CO;2-3
67. Vergne C, Boury-Esnault N, Perez T, Martin MT, Adeline MT, Dau ETH, Al-Mourabit A. Verpacamides A-D, a sequence of C11N5 diketopiperazines relating cyclo(Pro-Pro) to cyclo(Pro-Arg), from the marine sponge Axinella vaceleti: Possible biogenetic precursors of pyrrole-2- aminoimidazole alkaloids. Org Lett. 2006; 8(11):2421–2424. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ol0608092
68. Karanam G, Arumugam MK. Reactive oxygen species generation and mitochondrial dysfunction for the initiation of apoptotic cell death in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by a cyclic dipeptide Cyclo(-Pro-Tyr). Mol Biol Rep. 2020; 47(5):3347–3359. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05407-5
69. Narayana R, Mohana C, Kumar A. Analytical characterization of erucamide degradants by mass spectrometry. Polym Degrad Stab. 2022; 200:109956. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2022.109956
70. Brinkmann CM, Marker A, Kurtböke DI. An overview on marine sponge-symbiotic bacteria as unexhausted sources for natural product discovery. Diversity. 2017; 9(4):40. Doi: 10.3390/d9040040 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/d9040040
71. Liang J, She J, Fu J, Wang J, Ye Y, Yang B, Liu Y, Zhou X, Tao H. Advances in Natural Products from the Marine-Sponge-Associated Microorganisms with Antimicrobial Activity in the Last Decade. Mar Drugs. 2023; 21(4):236. Doi: 10.3390/md21040236 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/md21040236
72. Norouzi P, Mirmohammadi M, Houshdar Tehrani MH. Anticancer peptides mechanisms, simple and complex. Chem Biol Interact. 2022; 368:110194. Doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110194 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.110194
73. Koochaki R, Amini E, Zarehossini S, Zareh D, Haftcheshmeh SM, Jha SK, Kesharwani P, Shakeri A, Sahebkar A. Alkaloids in Cancer therapy: Targeting The Tumor Microenvironment and Metastasis Signaling Pathways. Fitoterapia. 2024; 179:106222. Doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106222 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fitote.2024.106222
74. Caesar LK, Cech NB. Synergy and Antagonism in Natural Product Extracts: When 1 + 1 Does Not Equal 2. Nat Prod Rep. 2019; 36(6):869–888. Doi: 10.1039/c9np00011a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NP00011A
75. Herranz-López M, Losada-Echeberría M, Barrajón-Catalán E. The Multitarget Activity of Natural Extracts on Cancer: Synergy and Xenohormesis. Medicines. 2018; 6(1):6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines6010006
76. Gowrishankar S, Sivaranjani M, Kamaladevi A, Ravi AV, Balamurugan K, Karutha Pandian S. Cyclic dipeptide cyclo(l-leucyl-l-prolyl) from marine Bacillus amyloliquefaciens mitigates biofilm formation and virulence in Listeria monocytogenes. Pathog Dis. 2016; 74(4):ftw017. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/femspd/ftw017
77. Aertgeerts K, Skene R, Yano J, Sang BC, Zou H, Snell G, Jennings A, Iwamoto K, Habuka N, Hirokawa A, Ishikawa T, Tanaka T, Miki H, Ohta Y, Sogabe S. Structural analysis of the mechanism of inhibition and allosteric activation of the kinase domain of HER2 protein. J Biol Chem. 2011; 286(21):18756–18765. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.206193
78. Ishikawa T, Seto M, Banno H, Kawakita Y, Oorui M, Taniguchi T, Ohta Y, Tamura T, Nakayama A, Miki H, Kamiguchi H, Tanaka T, Habuka N, Sogabe S, Yano J, Aertgeerts K, Kamiyama K. Design and synthesis of novel human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)/epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) dual inhibitors bearing a pyrrolo[3,2-d]pyrimidine scaffold. J Med Chem. 2011; 54(23):8030–8050. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm2008634
79. Wang S, Griffiths G, Midgley CA, Barnett AL, Cooper M, Grabarek J, Ingram L, Jackson W, Kontopidis G, McClue S, McInnes C, McLachlan J, Meades C, Mezna M, Stuart I, Thomas M, Zheleva D, Lane D, Jackson R, Glover D, Blake D, Fischer P. Discovery and characterization of 2-anilino-4- (thiazol-5-yl)pyrimidine transcriptional CDK inhibitors as anticancer agents. Chem Biol. 2010; 17(10):1111–1121. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.07.016
80. Wei H, Ruthenburg AJ, Bechis SK, Verdine GL. Nucleotide-dependent domain movement in the ATPase domain of a human type IIA DNA topoisomerase. J Biol Chem. 2005; 280(44):37041–37047. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M506520200
81. An L, Lin Y, Li L, Kong M, Lou Y, Wu J, Liu Z. Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation to Investigate the Effects and Mechanism of Astragalus Flavonoids Against Hepatic Fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 11:618262. Doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.618262 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.618262
82. Uzzaman M, Chowdhury MK, Belal Hossen M. Thermochemical, Molecular docking and ADMET studies of Aspirin metabolites. Front Drug Chem Clin Res. 2019; 2(3):1-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15761/FDCCR.1000130
83. Mohanty M, Mohanty PS. Molecular Docking in Organic, Inorganic, and Hybrid Systems: A Tutorial Review. Monatsh Chem. 2023; 154:683–707. Doi: 10.1007/s00706-023-03076-1 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00706-023-03076-1
84. Morris GM, Ruth H, Lindstrom W, Sanner MF, Belew RK, Goodsell DS, Olson AJ. Software news and updates AutoDock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J Comput Chem. 2009; 30(16):2785–2791. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21256
85. Kastritis PL, Bonvin AMJJ. On the binding affinity of macromolecular interactions: Daring to ask why proteins interact. J R Soc Interface. 2012; 10(79):20120835. Doi: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0835 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2012.0835
86. Martins MB, Carvalho I. Diketopiperazines: biological activity and synthesis. Tetrahedron. 2007; 63(40): 9923–9932. Doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2007.04.105 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2007.04.105
87. Borthwick AD. 2,5-diketopiperazines: Synthesis, reactions, medicinal chemistry, and bioactive natural products. Chem Rev. 2012; 112(7):3641-3716. doi: 10.1021/cr200398y DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200398y
88. Schmidt K, Gunther W, Stoyanova S, Schubert B, Li Z, Hamburger M. Militarinone A, a neurotrophic pyridone alkaloid from Paecilomyces militaris. Org Lett. 2002; 4(2):197–199. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ol016920j
89. Larsen Wilson MR, Taylor RE. Conformation-activity relationships of polyketide natural products. Nat Prod Rep. 2015; 32(8):1183–1206. Doi: 10.1039/c5np00014a DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NP00014A
90. Küenzi P, Kiefer S, Koryakina A, Hamburger M. Promotion of cell death or neurite outgrowth in PC-12 and N2a cells by the fungal alkaloid militarinone a depends on basal expression of p53. Apoptosis. 2008; 13(3):364–376. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0185-x
91. Aleti G, Sessitsch A, Brader G. Genome Mining: Prediction of Lipopeptides and Polyketides from Bacillus and Related Firmicutes. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2015; 13:192–203. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csbj.2015.03.003
92. Singh A, Mukhopadhyay K, Ghosh Sachan S. Biotransformation of eugenol to vanillin by a novel strain Bacillus safensis SMS1003. Biocatal Biotransformation. 2019; 37(4):291–303. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/10242422.2018.1544245
93. Slomka S, Françoise I, Hornung G, Asraf O, Biniashvili T, Pilpel Y, Dahan O. Experimental Evolution of Bacillus subtilis Reveals The Evolutionary Dynamics of Horizontal Gene Transfer and Suggests Adaptive and Neutral Effects. Genetics. 2020; 216(2):543–558. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.120.303401