Acute Oral Toxicity of Grewia mollis Stem Bark Extract in Wistar Rats
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v9i8.68Keywords:
Rat, Oral, Stem bark, Grewia mollis, Acute toxicityAbstract
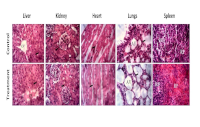
Grewia mollis is a medicinal plant and natural food additive and belongs to the family Malvaceae. The utilisation of the plant in traditional folk medicine is employed for the treatment of various diseases. Furthermore, it functions as a binding agent in numerous locally produced food products. Nevertheless, the available data about its safety is inadequate. The acute oral toxicity of G. mollis stem bark extract was determined in female Wistar rats using a fixed-dose procedure. Ten (10) female Wistar rats were allocated into two groups. G. mollis stem bark extract was administered orally to one group at 2000 mg/kg of body weight, while the other group (the control) received distilled water. There was no death in either the extract-treated or control groups. Therefore, the median lethal dose (LD50) of the G. mollis stem bark extract was considered greater than 2000 mg/kg of body weight.G. mollis stem bark elevated alkaline phosphatase activity and reduced serum cholesterol levels.It also increased serum total protein and sodium levels. However, no gross or histopathologic lesions were found in any of the examined organs. These results indicate that oral administration of G. mollis stem bark extract had no toxicological effects in rats and support the potential use of the stem bark extract as a safe natural food additive and therapeutic option.
References
Obidah W, Godwin JL, Fate JL Madusolumuo MA. Toxic effects of Grewia mollis stem bark in experimental rats. J. Am Sci. 2010; 6(12):1544-1548. https://doi.org/10.7537/marsjas050609.03.
Ogaji IJ, Hoag SW. Effect of grewia gum as a suspending agent on ibuprofen paediatric formulation. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2011;12(2): 507-513. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-011-9606-1.
Sambo SH, Olatunde A, Shaltoe SM (2015). Phytochemical screening and mineral analysis of Grewia mollis stems Bark. Int. J. Biochem. Res. Rev. 2015; 6(2): 75-81. https://doi.org/10.9734/IJBCRR/2015/14162
Kawasaki M, Sakuma S. Traditional and modern Japanese beers: methods of production and composition. In: Preedy VR (Ed). Beer in health and disease prevention. Burlington: Academic press; 2009. 45-52.
Nep EI, Odumosu PO, Ngwuluka NC, Olorunfemi PO, Ochekpe NA. Pharmaceutical properties and applications of a natural polymer from Grewia mollis. J. Polym. 2013;1-8.https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/938726.
Al-Asmari AK, Al-Elaiwi AM, Athar MT, Tariq M, Al Eid A, Al-Asmary SM. A review of hepatoprotective plants used in saudi traditional medicine. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014; 890842.https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/890842.
Adamu II, Adebayo SA, Al-Shahrani MS. Grewia mollis leaf extracts and fractions demonstrated good inhibitory activity on pro-inflammatory enzymes and with lower cytotoxicity in vitro. J. Inflamm. Res. 2020; 13: 765-772. https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S271254
Olusola LF, Baba J, Muhammad IL. Medicinal plants for the treatment of malaria and typhoid diseases. J. Med. Plants Res. 2023; 17 (1): 16-27.https://doi.org/10.5897/JMPR2022.7249
Sati NME, Ahmed FAM. Botanical overview and chemical composition of some Grewia spp. “Gudeim plants” in Sudan. Open Sci. J. 2018; 3(1), January. https://doi.org/10.23954/osj.v%25vi%25i.1408
Shagal MH, Kubmarawa D, Idi Z. Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activity of roots, stem bark and leaf extracts of Grewia mollis.Afri. J. Biotechnol. 2012; 11 (51):11350-11353. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701595300.
Asuku O, Atawodi SE, Onyike E. Antioxidant, Hepatoprotective, and ameliorative effects of methanolic extract of leaves of Grewia mollis Juss on carbon tetrachloride–treated albino rats. J. Med. Food. 2012; 15 (1): 83-88.https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2010.0285.
Okunye OL, Adegboyega IP, Emeka IW, Winifred AO, Fasuyi OC. Antimicrobial activity of crude extract of Grewia mollis Smith (Malvaceae) on clinical Isolates of Escherichia coli from cases of diarrhea. Sierra Leone J. Biomed. Res. 2021; 13:36-43. http://dx.doi.org/10.4314/sljbr.v11i1.1
Pongri A, Igbe I. Acute and sub-chronic toxicity evaluations of aqueous extract from stem bark of Grewia mollis (Malvaceae) in rats. Herba Pol. 2017; 63 (3):35-47.https://doi.org/10.1515/hepo-2017-0017.
Onwuliri FC, Mawak JD, Wonang DL, Onwuliri EA. Phytochemical, toxicological and histopathological studies of some medicinal plants in Nigeria. Int. Res. J. Nat. Sci. 2006;2(3):225-229. https://doi.org/10.4314/ijonas.v2i3.36094.
National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. (8th ed). Washington, DC; National Academies Press; 2011.
Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). Acute oral toxicity- fixed dose procedure. OECD Guideline 420 for Testing of Chemicals. Paris; OECD Publishing; 2001.
Zarei L, Shahrooz R. Protective effects of cornus mas fruit extract on methotrexate-induced alterations in mice testicular tissue: evidences for histochemical and histomorphometrical changes in an animal model study. Vet. Res. Forum. 2019; 10 (4):307-313. https://doi.org/10.30466/vrf.2019.69516.1955.
Suvarna KS, Layton C, Bancroft JD. Bancroft’s theory and practice of Histological techniques. (8th ed). London; Elsevier; 2019.
Ahmed M. Acute toxicity (Lethal Dose 50 Calculation) of Herbal Drug Somina in rats and mice. Pharmacol Pharm. 2015; 6:185-189. https://doi.org/10.4236/pp.2015.63019.
Ghasemi A, Jeddi S, Kashfi K. The laboratory rat: age and body weight matter. EXCLI J. 2021; 20:1431-1445.https://doi.org/10.17179/excli2021-4072
Lai MN, Hsu HC, Ng LT. Safety assessment of the standardized aqueous extract from solid-state cultured Xylarianigripes (Wuling Shen) in rats. Clin. Phytoscience. 2021; 7(44):1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40816-021-00281-5.
Al-Bassam MM, Al-Saeed HH, Arif HS. Correlation of bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase in infantile patients with cholestasis. Med. J. Babylon 2019; 16:47-50.
Onofrio FQ, Hirschfield GM. The pathophysiology of cholestasis and its relevance to clinical practice. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020; 15 (3): 110-114. https://doi.org/10.1002/cld.894.
Levitt MD, Hapak SM, Levitt DG. Alkaline phosphatase pathophysiology with emphasis on the seldom-discussed role of defective elimination in unexplained elevations of serum ALP-A case report and literature review. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2022; 15:41–49. https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S345531.
Yu L, Liu Y, Wang S, Zhang Q, Zhao J, Zhang H, Narbad A, Tian F, Zhai Q, Chen W. Cholestasis: exploring the triangular relationship of gut microbiota-bile acid-cholestasis and the potential probiotic strategies. Gut Microbes 2023;15:1, 2181930. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2023.2181930.
Villiger M, Stoop R, Vetsch T, Hohenauer E, Pini E, Clarys P, Pereira F, Clijsen R. Evaluation and review of body fluids saliva, sweat and tear compared to biochemical hydration assessment markers within blood and urine. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018; 72:69-76. https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2017.136.
Li Q, Wang Y, Mao Z, Kang H, Zhou F. Serum sodium levels predict mortality in erderly acute kidney injury patients: a retrospective observational study. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021; 14:603-612.https://doi.org/10.2147/IJGM.S294644.
Akachukwu D, Anah JO, Alaebo PO, Onwuegbu CR, Wokoma P. Phytochemicals of Cynodondactylon and the Toxicological Effect of its Aqueous Extract on Wistar Rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res, 2022; 6(4):645-649. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v6i4.28
Lombardi G, Pietro MF, Naticchia A, Gambaro G. Serum sodium variability and acute kidney injury: a retrospective observational cohort study on a hospitalized population. Intern Emerg Med (2021) 16:617–624. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-020-02462-5
Marahrensa B, Damscha L, Lehmanna R, Matyukhina I, Patschana S, Patschana D. Increased serum sodium at acute kidney injury onset predicts in-hospital death. J Clin Med Res. 2023;15(2):90-98. https://doi.org/10.14740/jocmr4845
Jeong SM, Choi S, Kim K, Kim SM, Lee G, Park SY, Kim YY, Son JS, Yun JM, Park SM. Effect of change in total cholesterol levels on cardiovascular disease among young adults. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018; 7(12): 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.118.008819.
Jung E, Kong SY, Ro YS, Ryu HH, Shin SD. Serum cholesterol levels and risk of cardiovascular death: a systematic review and a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022; 19(14):1-12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19148272.
Khil J, Kim SM, Chang J, Choi S, Lee G, Son JS, Park SM, Keum N. Changes in total cholesterol level and cardiovascular disease risk among type 2 diabetes patients. Sci. Rep. 2023; 13:8342.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-33743-6
Kim H. J., Jeong S., Oh Y. H., Park S. J., Cho Y. and Park S. M. Changes in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol with risk of cardiovascular disease among initially high-density lipoprotein-high participants. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2023; 22:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12933-023-01805-8
Sellers RS, Morton D, Michael B, Roome N, Johnson JK, Yano BL, Perry R, Schafer K. Society of Toxicologic Pathology position paper: organ weight recommendations for toxicology studies. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007;35(5): 751-755. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926230701595300.
Lazic SE, Semenova E, Williams DP. Determining organ weight toxicity with Bayesian causal models: Improving on the analysis of relative organ weights. Sci. Rep. 2020; 10:6625.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-63465-y.
Chike-Ekwughe A, John-Africa LB, Adebayo AH, Ogunlana OO. Evaluation of the toxic effects of ethanolic leaf extract of Tapinanthus cordifolius in mice and rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res, 2023; 7(10):4965-4972. https://doi.org//10.26538/tjnpr/v7i10.37
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Tropical Journal of Natural Product Research

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.







