Toxicological Evaluation of Co-Administration of Odogwu Bitters and Goko Cleanser Herbal Drinks on the Kidney of Adult Male Wistar Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
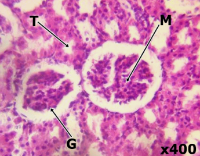
The consumption of herbal drinks is on the rise among Nigerians, especially within younger and artisan communities. This study investigates the potential histopathological impacts on kidney function when Odogwu Bitters and Goko Cleanser herbal drinks are co-administered to adult male Wistar rats. Forty male adult Wistar rats were used in the study, organized into ten groups with four rats each. Group A served as the control, while groups B, C, and D received 0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 ml of Odogwu Bitters, respectively. Groups E, F, and G received 0.2, 0.5, and 0.9 ml of Goko Cleanser, respectively. Groups H, I, and J received varying doses of both Odogwu Bitters and Goko Cleanser. The experiment was conducted over six weeks. At the end of the six-week period, blood samples were drawn for kidney function analysis, and the kidneys were collected for histological examination. The histological analysis indicated that co-administration of Odogwu Bitters and Goko Cleanser did not cause noticeable structural damage to the kidneys of adult male Wistar rats within the study period. However, biochemical analysis revealed that increasing doses of the herbal drinks led to significant changes in serum creatinine, urea, and uric acid levels (p = .001 for each parameter). This suggests that while no structural damage was observed in kidney tissue, the biochemical markers indicate potential renal effects at higher doses. The findings highlight the importance of cautious consumption of these herbal drinks to avoid potential kidney-related issues.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
1. Ekor M. The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front Pharmacol. 2014; 4: 177.
2. Anyanwu MU, Okoye RC. Antimicrobial activity of Nigerian medicinal plants. J. Intercult Ethnopharmacol. 2017; 6 (2): 240-259.
3. Chandrasekara A, Shahidi F. Herbal beverages: Bioactive compounds and their role in disease risk reduction - A review. J. Tradit Complement Med. 2018; 8 (4): 451-458.
4. Chan KT, Wu HY, Tin WY, But PP, Cheung SC, Shaw P. Ethnopharmacology of five flowers herbal tea, a popular traditional beverage in Hong Kong and South China. J. Ethnobiol Ethnomed. 2024; 20: 36.
5. Shaik MI, Hamdi IH, Sarbon NM. A comprehensive review on traditional herbal drinks: Physicochemical, phytochemicals and pharmacology properties. Food Chem Adv. 2023; 3: 100460.
6. Lim PHC. Asian herbals and aphrodisiacs used for managing ED. Transl Androl Urol. 2017; 6 (2): 167-175.
7. Saeed M, Munawar M, Bi JB, Ahmed S, Ahmad MZ, Kamboh AA, Arain MA, Naveed M, Chen H. Promising phytopharmacology, nutritional potential, health benefits, and traditional usage of Tribulus terrestris L. herb. Heliyon. 2024; 10 (4): e25549.
8. Martínez-Francés V, Rivera D, Obon C, Alcaraz F, Ríos S. Medicinal plants in traditional herbal wines and liquors in the East of Spain and the Balearic Islands. Front Pharmacol. 2021; 12: 713414.
9. Osuide GE. Regulation of herbal medicines in Nigeria: the role of the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC). In: Iwu MM, Wootton JC (eds). Adv Phytomed. Elsevier. 2002; 1: 249-258.
10. Dahiru M. Odogwu Bitters: Nigerian brew making waves around the world [Internet]. 2022. Retrieved from: https://www.premiumtimesng.com/opinion/549136-odogwu-bitters-nigerian-brew-making-waves-around-the-world-by-majeed-dahiru.html?tztc=1.
11. Onyejike DN, Aladeyelu OS, Onyejike IM, Nwankwo OK. Biochemical effects of Goko Cleanser herbal mixture on the kidney of adult female Wistar rats. Int Invention Sci J. 2018; 2 (4): 117-129.
12. Onyejike DN, McWilliams WC, Mmaju CI, Okeke SM, Obiesie IJ, Eze CE. Hematological study on the effects of Goko Cleanser (herbal mixture) on adult female Wistar rats. Int Blood Res Rev. 2021; 12 (1): 8–19.
13. Onyejike DN, Aladeyelu SO, Onyejike IM. Histopathological effects of Goko Cleanser (herbal mixture) on the kidney of adult female Wistar rats. Int J. Innov Res Adv Stud. 2018; 5 (6): 254–262.
14. Okaiyeto K, Oguntibeju OO. African herbal medicines: adverse effects and cytotoxic potentials with different therapeutic applications. Int J. Environ Res Public Health. 2021; 18 (11): 5988.
15. Byard R, Maker G, Musgrave I, Bunce M. What risks do herbal products pose to the Australian community? Med J. Aust. 2017; 206 (2): 134–134.
16. Asif M. A brief study of toxic effects of some medicinal herbs on kidney. Adv Biomed Res. 2012; 1: 44.
17. Dalley AF, Agur A. Moore’s Clinically Oriented Anatomy. 9th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2023: 308-320.
18. Murray IV, Paolini MA. Histology, kidney and glomerulus. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023. Retrieved from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554544/.
19. Radi ZA. Kidney pathophysiology, toxicology, and drug-induced injury in drug development. Int J. Toxicol. 2019; 38 (3): 215-227.
20. Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, et al. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021; 7: 52.
21. Liheluka E, Gibore NS, Lusingu JPA, et al. Community perceptions on the effectiveness of herbal medicines and factors associated with their use in managing diarrhea among under-five children in North-eastern Tanzania. Trop Med Health. 2023; 51: 48.
22. OECD. Test No. 425: Acute Oral Toxicity – Up-and-Down Procedure. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4. Paris: OECD Publishing; 2008. Available from: 10.1787/9789264071049-en.
23. AVMA. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition. 2020. Available from: https://www.avma.org/sites/default/files/2020-02/Guidelines-on-Euthanasia-2020.pdf.
24. Mathivha PL, Msagati TAM, Thibane VS, Mudau FN. Phytochemical analysis of herbal teas and their potential health, and food safety benefits: a review. In: Sen S, Chakraborty R (eds). Herbal Med. India. Springer, Singapore; 2020.
25. Onyejike DN, Aladeyelu SO, Onyejike IM, Ogbo FO. Effects of Goko Cleanser herbal mixture on the microarchitecture of the liver of adult female Wistar rats. Int Invention Sci. J. 2018; 2 (5): 184–200.
26. Onyejike DN, Aladeyelu SO, Onyejike IM, Nwankwo OK. Biochemical effects of Goko Cleanser (herbal mixture) on the liver of adult female Wistar rats. Int. Invention Sci J. 2018; 2 (5): 164–176.
27. Zhang L, Wang J, Zhang T, Li Y, Liu Z, Zhang X, Chen S. Protective effects of flavonoids on kidney injury: An overview of their mechanisms. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2018; 70 (10): 1357-1373.
28. Liu J, Yang M, Li Y, Wang X, Li Z, Li S, Zhang Y. Saponins as nephroprotective agents: Mechanisms and therapeutic potential. J Nat Prod. 2017; 80 (7): 1556-1563.
29. Saravanan G, Pugalendi KV. Protective effects of flavonoids on kidney function. Indian J Pharmacol. 2015; 47 (4): 370-376.
30. Ekor M, Umoren O, Usen A, Essien U, Usman M, Nwokeji F, Ononogbu A. Nephroprotective properties of saponins: A review. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2013; 21 (1): 1-8.
31. Sharma A, Kumar A, Singh H, Jain S, Sharma M, Kaur P, Verma R. Effects of herbal formulations on body weight and organ development. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020; 20 (1): 1-9.