Enhanced Extraction of Antishigellosis Compounds from Ficus elastica Leaves: A Response Surface Methodology Approach
Main Article Content
Abstract
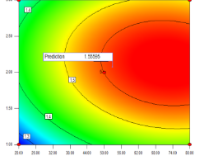
The leaves of Ficus elastica Roxb. ex Hornem exhibit strong antishigellosis activity against Shigella dysenteriae. This study investigated the effects of varying reflux conditions, including temperature and time, using response surface methodology (RSM) to optimize the extraction of antishigellosis compounds. Reflux conditions for F. elastica leaf extraction were designed using the Central Composite Design (CCD) method under RSM. A total of nine variations in reflux conditions were generated, with temperature ranging from 20°C to 80°C and time ranging from 1 to 3 h. The agar diffusion method was employed to evaluate the antibacterial activity of the extracts against S. dysenteriae ATCC 13313, with inhibition zone diameters used as the response variable. The interaction between temperature and time was analyzed using ANOVA. Optimization using RSM demonstrated that under optimal conditions (50°C and 2 h), the extraction yield increased significantly by 165.65%, achieving a yield of 16.23% (w/w) compared to 6.11% (w/w) under standard conditions. Furthermore, the antibacterial activity against Shigella spp. improved by 54.55%, with the inhibition zone diameter increasing from 11 mm under normal conditions to 17 mm under optimal conditions. This study highlights the importance of determining precise reflux parameters tailored to the sample and target compounds to enhance extraction efficiency and bioactivity.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Al-Dahmoshi H, Al-Khafaji, Al-Allak M, Salman W, Alabbasi, A. A review on shigellosis: pathogenesis and antibiotic resistance. Drug Invent Today. 2020; 14(5): 793–798.
Khalil IA, Troeger C, Blacker BF, Rao PC, Brown A, Atherly DE, Brewer TG, Engmann CM, Houpt ER, Kang G. Morbidity and mortality due to Shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea: the global burden of disease study 1990–2016. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018; 18(11): 1229–1240.
Aslam A, Okafor CN. Shigella. Treasure Island, FL, USA: StatPearls Publishing; (2022).
World Health Organization (WHO). Global Priority Pathogens. Geneva: WHO; 2021.
Ranjbar R, Farahani A. Shigella: antibiotic-resistance mechanisms and new horizons for treatment. Infect Drug Resist. 2019; 12: 3137–3167.
Singh B, Sharma SA. Updated review on Indian Ficus species. Arab J Chem. 2023; 16(8): 1-55.
Preeti, Abhishek J, Gaurav K, Loganathan K, Kokati VBR. Phytochemical composition and antioxidant activity of Ficus Elastica Roxb. (Moraceae) leaves. Res J Pharm Technol. 2015; 8(3):259-264.
Muhammad AH, Murniana M, Hira H, Nuraini N. Antimicrobial activity of n-hexane extracts of red frangipani (Plumeria rocea). J Nat. 2013; 13(1): 28-33.
Li P, Yin ZQ, Li SL, Huang XJ, Ye WC, Zhang QW. Simultaneous deter mination of eight favonoids and pogostone in Pogostemon cablin by high performance liquid chromatography. J Liq Chromatog Relat Technol. 2014; 37(12): 1771–1784.
Yi Y, Zhang QW, Li SL, Wang Y, Ye WC, Zhao J, Wang YT. Simultaneous quantification of major favonoids in Bawanghua, the edible fower of Hylocereus undatus using pressurised liquid extraction and high performance liquid chromatography. Food Chem. 2012; 135(2): 528–533.
Zhou YQ, Zhang QW, Li SL, Yin ZQ, Zhang XQ, Ye WC. Quality evaluation of semen oroxyli through simultaneous quantifcation of 13 components by high performance liquid chromatography. Curr Pharm Anal. 2012; 8(2): 206–213.
Du G, Zhao HY, Song YL, Zhang QW, Wang YT. Rapid simultaneous determination of isofavones in Radix puerariae using high-perfor mance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry with novel shell-type column. J Sep Sci. (2011); 34(19): 2576–2585.
Kongkiatpaiboon S, Gritsanapan W. Optimized extraction for high yield of insecticidal didehydrostemofoline alkaloid in Stemona collinsiae root extracts. Ind Crops Prod. 2013; 41: 371–374.
Zhang L. Comparison of extraction efect of active ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine compound preparation with two diferent method. Heilongjiang Xumu Shouyi. 2013; 9: 132–133.
Majeed M, Hussain AI, Chatha SAS, Khosa MKK, Kamal GM, Kamal MA, Zhang X, Liu M. Optimization protocol for the extraction of antioxidant components from Origanum vulgare leaves using response surface methodology. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2016; 23(3): 389–396.
Lee JW, Mo EJ, Choi JE, Jo YH, Jang H, Jeong JY, Jin Q, Chung HN, Hwang BY, Lee MK. Effect of Korean Red Ginseng extraction conditions on antioxidant activity, extraction yield, and ginsenoside Rg1 and phenolic content: optimization using response surface methodology. J Ginseng Res. 2016; 40(3): 229–236.
Hammi KM, Jdey A, Abdelly C, Majdoub H, Ksouri R. Optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction of antioxidant compounds from Tunisian Zizyphus lotus fruits using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2015; 184: 80–89.
Wu X, Yu X, Jing H. Optimization of phenolic antioxidant extraction from wuweizi (Schisandra chinensis) pulp using random-centroid optimization methodology. Int J Mol Sci. 2011; 12: 6255–6266.
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Goudarzi A, Soylak M, Mehdizadeh S, Langroodi. Magnetic nanoparticle based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction for the determination of malachite green in water samples: optimized experimental design. New J Chem. 2015; 39: 9813–9823.
Chauhan V, Dhiman V, Kanwar SS. Combination of classical and statistical approaches to enhance the fermentation conditions and increase the yield of Lipopeptide(s) by Pseudomonas sp. OXDC12: its partial purification and determining antifungal property. Turk J Biol. 2021; 45(6): 695-710.
Amado IR, Franco D, Sánchez M, Zapata C, Vázquez JA. Optimisation of antioxidant extraction from Solanum tuberosum potato peel waste by surface response methodology. Food Chem. 2014; 165: 290–299.
Ijoma KI, Ajiwe VIE, Ndubuisi JO. Evidenced based preferential in vitro antisickling mechanism of three Nigerian herbs used in the management of sickle cell disease. Malays J Biochem Mol Biol. 2023; 3: 9-17.
Kusuma SAF, Mita SR, Firdayani I, Mustarichie R. Study on the antibacterial activity of fruit extracts of klutuk banana (Musa balbisiana colla) against Shigella dysenteriae ATCC 13313. Asian J Pharm Clin Res. 2017; 10(7): 220-223.
Gil-Martín E, Forbes-Hernández T, Romero A, Cianciosi D, Giampieri F, Battino M. Influence of the extraction method on the recovery of bioactive phenolic compounds from food industry by-products. Food Chem. 2022; 378: 1-39.
Tan SP, Parks SE, Stathopoulos CE, Roach PD. Extraction of flavonoids from bitter melon. Food Nutr Sci. 2014; 5(5): 458-465.
Qu W, Pan Z, Ma H. Extraction modeling and activities of antioxidants from pomegranate Marc. J Food Eng. 2010; 99: 16–23.
Tušek AJ, Benković M, Cvitanović AB, Valinger D, Jurina T, Kljusurić JG. Kinetics and thermodynamics of the solid-liquid extraction process of total polyphenols, antioxidants and extraction yield from asteraceae plants. Ind Crops Prod. 2016; 91: 205–214.
Tchabo W, Ma Y, Kwaw E, Xiao L, Wu M, Apaliya M. Impact of extraction parameters and their optimization on the nutraceuticals and antioxidant properties of aqueous extract mulberry leaf. Int J Food Prop. 2018;21(1): 717–732.
Ignat I, Volf I, Popa VI. A critical review of methods for characterisation of polyphenolic compounds in fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2011; 126: 1821–1835.
Casazza AA, Aliakbarian B, Sannita E, Perego P. High-pressure high-temperature extraction of phenolic compounds from grape skins. Int J Food Sci Technol. 2012; 47: 399–405.
Mokrani A, Madani K. Effect of solvent, time and temperature on the extraction of phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity of peach (Prunus persica L.). fruit. Sep Purif Technol. 2016; 162: 68–76.
Garcia-Salas P, Morales-Soto A, Segura-Carretero A, Fernández-Gutiérrez A. Phenolic-compound-extraction systems for fruit and vegetable samples. Molecules. 2010; 15(12): 8813–8826.
Carrera C, Ruiz-Rodríguez A, Palma M, Barroso CG. Ultrasound assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from grapes. Anal chim acta. 2012; 732: 100–104.
Gao M, Wang XL, Gu M, Su ZG, Wang Y, Janson JC. Separation of poly phenols using porous polyamide resin and assessment of mechanism of retention. J Sep Sci. 2011; 34(15):1853–1858.
Scalbert A. Antimicrobial properties of tannins. Phytochem. 1991; 30: 3875-3883.
Miao J, Fan Y, Zhao C, Mao X, Chen X, Huang H, Gao W. Efect of diferent solvents on the chemical composition, antioxidant activity and alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity of hawthorn extracts. Intl J Food Sci Technol. 2016; 51(5): 1244–1251.
Shah SR, Ukaegbu CI., Hamid HA, Alara OR. Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial activities of the stems of Flammulina velutipes and Hypsizygus tessellatus (white and brown var.) extracted with diferent solvents. J Food Meas Food Charact. 2018; 12(3): 1947–1961.
Ashok PH, Upadhyaya K. Tannins are astringent. J Pharmacogn Phytochem. 2012; 1(3): 45-50.
Mahizan NA, Yang SK, Moo CL, Song AA, Chong CM, Chong CW, Abushelaibi A, Lim SHE, Lai KS. Terpene derivatives as a potential agent against antimicrobial resistance (amr) pathogens. Molecules. 2019; 24(14): 1-21.
Kolbeck S, Reetz L, Hilgarth M, Vogel RF. Quantitative oxygen consumption and respiratory activity of meat spoiling bacteria upon high oxygen modified atmosphere. Front Microbiol. 2019; 10: 1-12.
Cankaya IIT, Somuncuoglu EI. Potential and prophylactic use of plants containing saponin-type compounds as antibiofilm agents against respiratory tract infections. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021; 23: 1-14.
Liu Y, Lin-Wang K, Espley RV, Wang L, Li Y, Liu Z, Zhou P, Zeng L, Zhang X, Zhang J, Allan AC. StMYB44 negatively regulates anthocyanin biosynthesis at high temperatures in tuber flesh of potato. J Exp Bot. 2019; 70: 3809–3824.
Weirong C, Xiaohong G, Jian T. Extraction, purification, and characterization of the flavonoids from opuntia milpa alta skin. Czech J Food Sci. 2010; 28(2); 108–116.
Settharaksa S, Jongjareonrak A, Hmadhlu P, Chansuwan W, Siripongvutikorn S. Flavonoid, phenolic contents and antioxidant properties of Thai hot curry paste extract and its ingredients as affected of pH, solvent types and high temperature. Int Food Res J. 2012; 19(4): 1581-1587.
Hiba N, Nada E, Zeina H, Nadia B, Eugene V, Richard GM, Louka N. Extraction of total phenolic compounds, flavonoids, anthocyanins and tannins from grape byproducts by response surface methodology. influence of solid-liquid ratio, particle size, time, temperature and solvent mixtures on the optimization process. Food Nutr Sci. 2014; 5(4): 397-409.
Fausto G, Vincenzo P. Temperature and solvent effects on polyphenol extraction process from chestnut tree wood. Chem Eng Res Des. 2011; 89(7): 857–862.
Lei WB, Ju-Wu H, Wei X, Xiong-Hui L, Guan-Hua W, Lin D, Hu W. Optimization of the extraction process for flavonoids from basil (Ocimum basilicum) using response surface methodology. J Bioresour Bioprod. 2016; 1(4): 177-185.
Mancinelli S, Turcato A, Kisslinger A, Bongiovanni A, Zazzu V, Lanati A, Ligouri GL. Design of transfections: Implementation of design of experiments for cell transfection fine tuning. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2021; 118(11): 4488-4501.
Wahid Z, Nadir N. Improvement of one factor at a time through design of experiments. World Appl Sci J. 2013; 21(special issue 1): 56–61.
Anuar N, Mohd Adnan AF, Saat N, Aziz N, Taha RM. Optimization of extraction parameters by using response surface methodology, purification, and identification of anthocyanin pigments in Melastoma malabathricum fruit. Sci World J. 2013; 2013: 1-10.
Aourabi S, Sfaira M, Mahjoubi F. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenol content from Zea mays Hairs (waste). Sci World J. 2020; 2020: 1-10.
Abu Bakar FI, Abu Bakar MF, Abdullah N, Endrini S, Fatmawati S. Optimization of extraction conditions of phytochemical compounds and anti-gout activity of Euphorbia hirta L. (Ara Tanah) using response surface methodology and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) Analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020; 2020: 1-13.
Becze A, Babalau-Fuss VL, Varaticeanu C, Roman C. Optimization of high-pressure extraction process of antioxidant compounds from Feteasca regala leaves using response surface methodology. Molecules. 2020; 25(18): 1-14.
Ajayi GO, Idoko A, Usman A. Phytochemical analysis and antibacterial activity of Trema orientalis (Ulmaceae) stem bark extracts on respiratory tract bacteria. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2018; 2(12):512-516.