Prediction of Antiinflammatory Effects of Rosmarinus officinalis L. in Osteoarthritis Through Inhibition in PGE2-R, COX-2, and IL-1b: an In Silico Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
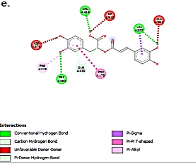
Osteoarthritis can cause inflammation, stiffness and pain in the joints. Phytochemical compounds of Rosmarinus officinalis L. (RO) such as Carnosol (CAR), Carnosic Acid (CA), Rosmarinic Acid (RA), and Micromeric Acid (MA) have been proven to be anti-inflammatory alternative drugs. This study was conducted to predict anti-inflammatory effects through the inhibition of several inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis such as Prostaglandin E2 Receptor (PGE2-R), Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and Interleukin 1 beta (IL-1β) by identifying the binding affinity, hydrogen bond distance, RMSDAll, and RMSDLigMove of ligand complexes with proteins. Phytochemical compounds of RO were subjected to molecular docking using PyRx 0.8 software with the AutoDock Vina method then analyzed using Biovia Discovery Studio Visualizer 2021 software. The results show that the binding affinity value of molecular docking ligands with PGE2-R showed CAR (-8.70 kcal/mol), CA(-7.30 kcal/mol), RA(-6.80 kcal/mol), and MA (-8.20 kcal/mol). The binding affinity values of molecular docking of ligands with COX-2 are in the following order: CAR (-7.90 kcal/mol), CA (-7.60 kcal/mol), RA (-7.20 kcal/mol), MA (-8.80 kcal/mol). The binding affinity values of molecular docking of ligands with IL-1β are in the following order: CAR (-8.20 kcal/mol), CA (-8.10 kcal/mol), RA (-6.60 kcal/mol), MA (-7.40 kcal/mol). Finally, a molecular dynamics simulation experiment using YASARA software showed that RMSDAll and RMSDLigMove values of the ligands were better than potassium diclofenac. The study concluded that the phytochemical compounds of Rosmarinus officinalis L could inhibit PGE2-R, COX-2, and IL-1b with more negative binding affinity than potassium diclofenac.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Kapoor M, Martel-Pelletier J, Lajeunesse D, Pelletier JPP; Fahmi H. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011; 7:33–42.
Scanzello CR. Chemokines and inflammation in osteoarthritis: Insights from patients and animal models. J. Orthop. Res. 2017; 35:735–739
Yorifuji M, Sawaji Y, Endo K, Kosaka T, Yamamoto K. Limited efficacy of COX-2 inhibitors on nerve growth factor and metalloproteinases expressions in human synovial fibroblasts. J Orthop Sci. 2016; 21:381e8
Zweers MC, de Boer TN, Van Roon J, Bijlsma JW, Lafeber FP, Mastbergen SC. Celecoxib: considerations regarding its potential disease-modifying properties in osteoarthritis. Arthr Res Ther. 2011; 13:239.
Martel-Pelletier J, Pelletier JP, Fahmi H. Cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandins in articular tissues. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 33:155e67
Nakata K, Hanai T, Take Y, Osada T, Tsuchiya T, Shima D, Fujimoto Y. Disease-modifying effects of COX-2 selective inhibitors and non-selective NSAIDs in osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2018; 26: 1263-1273.
Alhammadi N, Asiri AH, Alshahrani FM, Alqahtani FS, Alzahrani FA, Alshahrani A, Alshehri AM, Alqahtani AS, Alqahtani SA. Gastrointestinal Complications Associated with Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drug Use among Adults: A Retrospective, Single-Center Study. Cureus. 2022; 14: e26154.107759/cureus.26154
Hunter LJ, Wood DM, Dargan PI. The patterns of toxicity and management of acute nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) overdose. Open Access Emerg Med. 2011; 3:39-48
Sriuttha P, Sirichanchuen B, Permsuwan U. Hepatotoxicity of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int J Hepatol. 2018; 5253623.
Luo C, Zou L, Sun H, Peng J, Gao C, Bao L, Ji R, Jin Y and Sun S. A Review of Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Rosmarinic Acid on Inflammatory diseases. Front in Pharm. 2020;11: DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00153
Hu ZN, Huang LJ, and Chen WP. The inhibitory effects of rosmarinic acid on catabolism induced by IL-1βeta in rat chondrocyte. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2018; 65 (4), 535–538. doi: 10.18388/abp.2018_2607
Borrás LI, Pérez SA, Lozano SJ, Barrajón CE, Arráez RD, Cifuentes A, Micol V, Carretero SA. A bioguided identification of the active compounds that contribute to the antiproliferative/cytotoxic effects of rosemary extract on colon cancer cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015; 80: p.215–222. [PubMed: 25801906]
Agu PC, Afiukwa CA, Orji OU. Ezeh ME, Ofoke IH, Ogbu CO, Ugwuja EI, and Aja PM. Molecular docking as a tool for the discovery of molecular targets of nutraceuticals in disease management. Sci Rep. 2023; 13: 13398.
Das DR, Kumar D, Kumar P, and Dash BP. Molecular docking and its application in search of antisickling agent from Carica papaya. J Appl Biol Biotechnol. 2020; 8(01): 105–116.
Unke OT, Stöhr M, Ganscha S, Unterthiner T, Maennel H, Kashubin S, Ahlin D, Gastegger M, Medrano Sandonas L, Berryman JT, Tkatchenko A, Müller KR. Biomolecular dynamics with machine-learned quantum-mechanical force fields trained on diverse chemical fragments. Sci Adv. 2024; 10(14):eadn4397. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adn4397.
Krieger E, Vriend G. YASARA View—molecular graphics for all devices—from smartphones to workstations. Bioinf. 2014; 30(20):2981–2982
McConkey BJ, Sobolev V, Edelman M. The performance of current methods in ligand-protein docking. Curr Sci. 2002; 83:845–855
Meng XY, Zhang HX, Mezei M, Cui M. Molecular docking: a powerful approach for structure-based drug discovery. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2011; Jun 7(2):146-57. doi: 10.2174/157340911795677602. PMID: 21534921; PMCID: PMC3151162.
Hospital A, Goñi JR, Orozco M, Gelpí JL. Molecular dynamics simulations: advances and applications. Adv Appl Bioinform Chem. 2015; Nov 19 (8):37-47. Doi: 10.2147/AABC.S70333.
Wang L, Wu Y, Jia Z, Yu J and Huang S. Roles of EP Receptors in the Regulation of Fluid Balance and Blood Pressure. Front. Endocrinol. 2022; 13:875425. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.875425
Pérez-Fons L, Garzón MT, Micol V. Relationship between the antioxidant capacity and effect of rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.) polyphenols on membrane phospholipid order. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010; 58(1):161–171.
Megha KB, Joseph X, Akhil V, Mohanan PV. Cascade of immune mechanism and consequences of inflammatory disorders. Phytomed. 2021; Oct 9(1):153712.
Castro-Alvarez A, Costa AM, Vilarrasa J. The Performance of Several Docking Programs at Reproducing Protein-Macrolide-Like Crystal Structures. Molecules. 2017;22(1):136. doi: 10.3390/molecules22010136.
Itoh Y, Nakashima Y, Tsukamoto S, Kurohara T, Suzuki M, Sakae Y, Oda M, Okamoto Y, and Suzuki T. N+-C-H···O hydrogen bonds in protein-ligand complexes. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):1–12.
Pace CN, Fu H, Fryar KL, Landua J, Trevino SR, Schell D, Thurlkill RL, Imura S, Scholtz JM, Gajiwala K, Sevcik J, Urbanikova L, Myers JK, Takano K, Hebert EJ, Shirley BA, and Grimsley G.R. Contribution of hydrogen bonds to protein stability. Prot Sci. 2014; 23(5):652–661.
Motiejunas D, Wade RC. Structural, energetic, and dynamic aspects of ligand-receptor interactions. Comp Med Chem II. 2007; 4(8):114
Effendy. VSEPR Theory of Polarity and Intermolecular Forces. Bayumedia Publishing. Malang. 2006.
Herschlag D and Pinney MM. Hydrogen Bonds: Simple After All? Biochemistry. 2018; (24):3338-3352. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00217.