Characterization of Physicochemical Properties and Dissolution Studies of Multicomponent Crystals of Piperine and Glutamic Acid
Main Article Content
Abstract
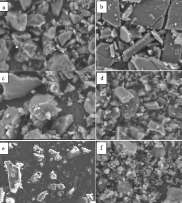
Piperine, a secondary metabolite compound, has a low solubility in water. In this study, through the formation of multicomponent crystals, glutamic acid is employed as a coformer to enhance the physicochemical characteristics and improve the dissolution rate of piperine. Solvent drop grinding was used to create multicomponent crystals using molar ratios of piperine and glutamic acid of 1:1 (F1), 1:2 (F2), and 2:1 (F3). Characterization of the solids’ properties was performed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and dissolution profiles in accordance with the United States Pharmacopoeia (USP), facilitating a comparison with the physical mixture and pure piperine. XRD results showed a decrease in intensity, and DSC showed a decrease in the endothermic peak transition temperature and significant decreases in enthalpy value. The FT-IR spectra showed a change in wave numbers, and no new functional groups were formed. SEM revealed changes in particle morphology forming new crystal habits. When contrasted with the physical mixture and pure piperine, the dissolution profiles of multicomponent crystals F1, F2, and F3 demonstrate increased dissolution rates, F2 exhibiting a 1.57-fold increase, followed by 1.44-fold for F1 and 1.49-fold for F3. Multicomponent crystals F1, F2, and F3 show a better dissolution profile than the physical mixture and pure piperine, with dissolved substance percentages of 63.60±6.56, 68.59±2.53, 65.25±12.10, 44.91±10.95, and 43.58±8.92, respectively, after 60 minutes at 37±0.5 °C. The multicomponent crystals produced using solvent drop grinding exhibited enhanced physicochemical features and an increased dissolution rate.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
References
Stielow M, Witczyńska A, Kubryń N, Fijałkowski Ł, Nowaczyk J, Nowaczyk A. The bioavailability of drugs-The current state of knowledge. Molecules. 2023; 28(24):1-19.
Kalepu S, Nekkanti V. Insoluble drug delivery strategis: review of recent advances and business prospects. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2015; 5(5):442-453.
Savjani KT, Gajjar AK, Savjani JK. Drug solubility: importance and enhancement techniques. ISRN Pharm. 2012; 2012:1–10.
He G, Chow PS, Tan RBH. Predicting multicomponent crystal formation: The interplay between homomeric and heteromeric interaction. Cryst Growth Des. 2009; 9(10):4529-4532.
Steed JW. The role of co-crystals in pharmaceutical design. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2013; 34(3):185–193.
Anggraini D, Zaini E. Multicomponent crystals of fenofibric acid-L-proline with enhanced dissolution rate and antihyperlipidemic activity. J Res Pharm. 2024; 28(4):974-981.
Mirza S, Heinamaki J, Miroshnyk I, Yliruusi J. Co-crystals : an emerging approach for enhancing properties of pharmaceutical solids. Dosis. 2008; 24(2):90–96.
Qiao N, Li M, Schlindwein W, Malek N, Davies A, Trappitt G. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: An overview. Int J Pharm. 2011; 419(1-2):1–11.
Sekhon B. Pharmaceutical co-crystals - a review. ARS Pharm. 2009; 50(3):99–117.
Aakeröy CB, Fasulo M, Schultheiss N, Desper J, Moore C. Structural competition between hydrogen bonds and halogen bonds. J Am Chem Soc. 2007; 129(45):13772–13773.
Vishweshwar P, McMahon JA, Bis JA, Zaworotko MJ. Pharmaceutical co-crystals. J Pharm Sci. 2006; 95(3):499–516.
Berry DJ, Steed JW. Pharmaceutical cocrystals, salts and multicomponent systems; intermolecular interactions and property-based design. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017; 117:3-24.
Zaini E, Afriyeni, Fitriani L, Ismed F, Horikawa A, Uekusa H. Improved solubility and dissolution rates in novel multicomponent crystals of piperine with succinic acid. Sci Pharm. 2020; 88(2):1-12 .
Sharma A, Jain CP, Ashawat MS. Biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS) and biowaivers: role in drug product design. Res J Pharm Technol. 2008; 1(3):144–151.
Vasavirama K, Upender M. Piperine: A valuable alkaloid from piper species. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. 2014; 6(4):34–38.
Ahmad N, Fazal H, Abbasi BH, Farooq S, Ali M, Khan MA. Biologogical role of Piper nigrum L. (Black Pepper): A Review. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012; 2(3): S1945-S1953.
Tilborg A, Norberg B, Wouters J. Pharmaceutical salts and cocrystals involving amino acids: A brief structural overview of the state-of-art. Eur J Med Chem. 2014; 74:411–426.
Nechipadappu SK, Tekuri V, Trivedi DR. Pharmaceutical co-crystal of flufenamic acid: synthesis and characterization of two novel drug-drug co-crystal. J Pharm Sci. 2017; 106(5):1384–1390.
Panzade P, Shendarkar G, Kulkarni D, Shelke S. Solid state characterization and dissolution enhancement of nevirapine cocrystals. Adv Pharm Bull. 2021; 11(4):772–776.
Octavia MD, Hasmiwati H, Revilla G, Zaini E. Multicomponent crystals of piperin-nicotinic acid: The physicochemical and dissolution rate properties. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2023; 7(8):3701-3705.
Zaini E, Wahyuni YS, Halim A, Yuliandra Y. Preparation of eutectic mixture of ketoprofen and nicotinamide for enhanced dissolution rate. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res. 2015; 35(1): 161–164.
Octavia MD, Hasmiwati H, Revilla G, Zaini E. Isolasi piperin dari lada hitam (Piper nigrum L.) dan uji kemurniannya. J Farm Higea. 2024; 16(1);52-62.
Zafrul A, Halim A, Mayariz A, Octavia MD. Komplek inklusi amlodipine besilat -β-siklodekstrin dengan metode co-grinding. J Farm Higea. 2024; 6(1): 25-33.
Gadade DD, Pekamwar SS. Pharmaceutical cocrystals: regulatory and strategic aspects, design and development. Adv Pharm Bull. 2016; 6(4):479–494.
DaSilva CC, Guimarães FF, Ribeiro L, Martins FT. Salt or cocrystal of salt? Probing the nature of multicomponent crystal forms with infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2016; 167:89-95.
Zaini E, Halim A, Soewandhi SN, Setyawan D. Peningkatan laju pelarutan trimetoprim melalui metode ko-kristalisasi dengan nikotinamida. J Farm Indones. 2011; 5(4):206–212.
Zaini E, Riska D, Oktavia MD, Ismed F, Fitriani L. Improving dissolution rate of piperine by multicomponent crystal formation with saccharin. Res J Pharm Tech. 2020; 13(4):1926-1930.
Wahyuni R, Lucida H, Revilla G, Ismed F, Zaini E. Preparation and characterization of usnic acid nanocrystals with the wet grinding method using a planetary ball mill. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2024; 8(1):5801–5805.
Elghani MA, Klapotke TM. A review on differential scanning calorimetry technique and its importance in the field of energetic materials. Physic Sci Rev. 2018; 3(4):1-14.
Sartinah A, Uekusa H, Abekura Y, Ibrahim S, Anggadiredja K, Nugrahani I, Piperine-hydroxybenzoate as phytochemistry antiosteoarthritis combination: structural, solubility, and in vivo antiinflammatory study, Heliyon. 2024; 10(11):1-11.
Singh J, Dutta PK, Dutta J, Hunt AJ, Macquarrie DJ, Clark JH. Preparation and properties of highly soluble chitosan-l-glutamic acid aerogel derivative. Carbohydr Polym. 2009; 76: 188–195.
Kumirska J, Czerwicka M, Kaczyński Z, Bychowska A, Brzozowski K, Thöming J, Stepnowski P. Application of spectroscopic methods for structural analysis of chitin and chitosan. Mar Drugs. 2010; 8(5):1567-1636.
Fitriani L, Simbolon CA, Zaini E. Preparation and characterization of multicomponent crystal piperine-caffeine. J Sains Farm Klin. 2023; 10(3):353–358.
Ullah N, Qazi RA, Ullah S, Khan S. Application and importance of scanning and transmission electron microscopes in science and technology. Contributions Sec Nat Math Biotech Sci. 2023; 43(1-2):27-37.