Anti-inflammatory, Analgesic, and Motor Improvement Effects of Bee Venom Acupuncture on Freund’s Complete Adjuvant-Induced Spinal Degeneration in Rats
Main Article Content
Abstract
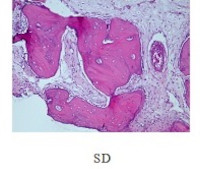
Spinal degeneration (SD) is a common condition among the elderly, causing pain and reduced mobility. Prompt detection, monitoring, and treatment of degenerative conditions is crucial to minimize serious complications. In this experiment, rats with Freund’s complete adjuvant (CFA)-induced SD received bee venom acupuncture (BVA) at doses of 0.5, 1.0, and 1.5 mg/kg or Mobic (meloxicam) acupuncture (MA) at 1.0 mg/kg. All treatments were administered twice weekly for three weeks. The anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and motor improvement effects of BVA were evaluated via behavioral tests, white blood cell counts, and histological analysis. Results showed significant reductions in white blood cell count and the inflammatory marker interleukin-1β (IL-1β) in both BVA and MA groups compared to the control SD group. Additionally, the BVA and MA treatment groups showed increased hotplate paw-withdrawal latency, indicating reduced pain sensitivity, and longer times on the accelerating rotarod, indicating improved motor function, compared to the control group. These findings suggest that BVA has promising anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and motor-improving effects for the symptomatic treatment of SD.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Anderson JT, Haas AR, Percy R, Woods ST, Ahn UM, Ahn NU. Lumbar diskography and failed back syndrome in patients receiving workers' compensation. Orthopedics. 2015; 38(11):e951-e958. https://doi.org/10.3928/01477447-20151020-01
Frymoyer JW. Lumbar disk disease: epidemiology. Instr Course Lect. 1992; 41:217-223.
Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, Blyth F, Woolf A, Bain C, Williams G, Smith E, Vos T, Barendregt J, Murray C, Burstein R, Buchbinder R. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014; 73(6):968-974. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204428
Wongrakpanich S, Wongrakpanich A, Melhado K, Rangaswami J. A comprehensive review of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in the elderly. Aging Dis. 2018; 9(1):143-150. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2017.0306
Falodun A, Okunrobo LO, Uzoamaka N. Phytochemical screening and anti-inflammatory evaluation of methanolic and aqueous extracts of Euphorbia heterophylla Linn (Euphorbiaceae). Afr J Biotechnol. 2006; 5(6):529-531.
Ching FP, Okpo SO, Falodun A, Omogbai EKI. Analgesic activities of fractions of Stereospermum kunthianum stem bark. Planta Med. 2009; 75(09):PJ187. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0029-1234992
Abdullahi ID, Yaro AH, Nazifi AB. Preliminary studies on the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of methanol leaf extract of Ficus asperifolia Miq. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2020; 4(3):85-90. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v4i3.5
Ajiboye OM, Adewumi A, Ogunwenmo KO, Animashaun R, Jegede DO, Aina FO. Pain alleviating potential of ethanol extract of Vernonia amygdalina Del. on writhing in male Wistar rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2024; 8(4):7000-7005. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v8i4.35
Uche ME, Chinyere CG, Ekweogu CN, Esiaba RI, Nwankpa P, Ugbogu EA. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory and anti-gastric ulcer potential of aqueous leaf extract of Emilia sonchifolia in rats. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2024; 8(9):8314-8320. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v8i9.10
Nhung TTP and Quoc LPT. Exploring the analgesic, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory properties of Annona squamosa Linnaeus fruit peel extract in a mouse model. Trop J Nat Prod Res. 2024; 8(9):8537-8545. https://doi.org/10.26538/tjnpr/v8i9.42
Zhang S, Liu Y, Ye Y, Wang XR, Lin LT, Xiao LY, Zhou P, Shi GX, Liu CZ. Bee venom therapy: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic applications. Toxicon. 2018; 148:64-73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.04.012
Sung SH, Lee HJ, Han JE, Sung ADM, Park M, Shin S, Jeong HI, Jang S, Lee J. Bee venom acupuncture for neck pain: A review of the Korean literature. Toxins (Basel). 2023; 15(2):129. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020129
Jiang H, Wang J, Xu B, Yang Q, Liu Y. Study on the expression of nerve growth associated protein-43 in rat model of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017; 17(2):104-107.
Lee JH, Kim KO, Kim KS, Park SY, Yang SJ, Choi CW, Na CS, Wei TS. Effects of sweet bee venom pharmacopuncture and low-level laser acupuncture on a rat model with complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis. Acupuncture. 2015; 32(3):1-13. https://doi.org/10.13045/acupunct.2015034
Banik RK, Sia T, Ibrahim MM, Sivanesan E, Uhelski M, Pena A, Streicher JM, Simone DA. Increases in local skin temperature correlate with spontaneous foot lifting and heat hyperalgesia in both incisional inflammatory models of pain. Pain Rep. 2023; 8(5):e1097. https://doi.org/10.1097/PR9.0000000000001097
Modi AD, Parekh A, Pancholi YN. Evaluating pain behaviours: Widely used mechanical and thermal methods in rodents. Behav Brain Res. 2023; 446:114417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2023.114417
Abdelghany AK, El-Kashlan AM, Emeash HH, Khalil F. Long-term scopolamine treatment altered locomotor, exploratory and anxiety-like behaviours of albino rats. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. 2022; 11(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43088-021-00187-8
Magdy A, Farrag EAE, Hamed SM, Abdallah Z, El Nashar EM, Alghamdi MA, Ali AAH, El-Kader MA. Neuroprotective and therapeutic effects of calcitriol in rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease rat model. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022; 16:967813. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2022.967813
Qin M and Qiu Z. Changes in TNF-α, IL-6, IL-10, and VEGF in rats with ARDS and the effects of dexamethasone. Exp Ther Med. 2019; 17(1):383-387. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2018.6926
Mosley GE, Wang M, Nasser P, Lai A, Charen DA, Zhang B, Iatridis JC. Males and females exhibit distinct relationships between intervertebral disc degeneration and pain in a rat model. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):15120. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72081-9
Aigner T, Cook JL, Gerwin N, Glasson SS, Laverty S, Little CB, McIlwraith W, Kraus VB. Histopathology atlas of animal model systems-overview of guiding principles. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(Suppl 3):S2-S6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2010.07.013
Petchi RR, Parasuraman S, Vijaya C, Gopala Krishna SV, Kumar MK. Antiarthritic activity of a polyherbal formulation against Freund's complete adjuvant induced arthritis in female Wistar rats. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2015; 6(3):77-83. https://doi.org/10.4103/0976-0105.160738
Kamarudin TA, Othman F, Ramli ESM, Isa NMd, Das S. Protective effect of curcumin on experimentally induced arthritic rats: detailed histopathological study of the joints and white blood cell count. EXCLI J. 2012; 11:226-236.
Wautier JL and Wautier MP. Pro- and anti-inflammatory prostaglandins and cytokines in humans: A mini review. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(11):9647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24119647
Kany S, Vollrath JT, Relja B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2019; 20(23):6008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236008
Huh JE, Seo BK, Lee JW, Park YC, Baek YH. Analgesic effects of diluted bee venom acupuncture mediated by δ-opioid and α2-adrenergic receptors in osteoarthritic rats. Altern Ther Health Med. 2018; 24(2):28-35.
Cheng X, Xiao F, Xie R, Hu H, Wan Y. Alternate thermal stimulation ameliorates thermal sensitivity and modulates calbindin-D 28K expression in lamina I and II and dorsal root ganglia in a mouse spinal cord contusion injury model. FASEB J. 2021; 35(2):e21173. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.202001775R
Xiang, HC, Lin LX, Hu XF, Zhu H, Li HP, Zhang RY, Hu L, Liu WT, Zhao YL, Shu Y, Pan HL, Li M. AMPK activation attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation and IL-1β expression. J Neuroinflammation. 2019; 16(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1411-x
Stela M, Cichon N, Spławska A, Szyposzynska M, Bijak M. Therapeutic potential and mechanisms of bee venom therapy: A comprehensive review of apitoxin applications and safety enhancement strategies. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024; 17(9):1211. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph17091211
Seo DM, Park DS, Kang SG. The analgesic effect of bee venom aqua acupuncture and its mechanism in the rat model with adjuvant-induced arthritis. J Kor Acu Mox Soc. 2003; 20(2):85-97.
Klinghardt DK. Bee venom therapy for chronic pain. J Neurol Orth Med Surg. 1990; 11(3):195-197.
Lim BS, Moon HJ, Li DX, Gil M, Min JK, Lee G, Bae H, Kim SK, Min BI. Effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced cold allodynia in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013; 2013:369324. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/369324
Kim JS, Kroin JS, Li X, An HS, Buvanendran A, Yan D, Tuman KJ, van Wijnen AJ, Chen D, Im HJ. The rat intervertebral disk degeneration pain model: relationships between biological and structural alterations and pain. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011; 13(5):R165. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3485